Engineering Drawing
Engineering Drawing, All Module
Engineering Drawing
⭕️ Show all Answers
Q1: A French curve is used to draw
- Circles
- Smooth freeform curve
- Right circular cone
- Orthographic projection
Q2: Name the curve which has Zero eccentricity
- Circle
- Parabola
- Hyperbola
- Ellipse
Q3: Lettering of drawing sheet should have –
- In a sentence only first alphabet in capital letters
- All alphabets in small letters
- In a sentence only abbreviations in capital letters
- All alphabets in capital letters
Q4: To lay off an angle from a given line, what marks on the protector should your align for higher accuracy-
- Centre mark and 0 marks only
- 00 and 1800 marks only
- 00, 1800 and centre marks
- 00, 900 and 1800 marks
Q5: Which of the following pairs of orthographic views both show the height dimension?
- Top and Front
- Front and Side
- Top and Rear
- Bottom and Right side
Q6: The recommended symbol for indicating the angle of projection shows two views of the frustum of a –
- Square Pyramid
- Triangle Pyramid
- Cone
- Any of these
Q7: The projection in isometric view are –
- Converging
- Parallel to the plane of projection
- Diverging
- Perpendicular to the plane of projection
Q8: “Principles of folding of drawing prints” are laid down in IS: _______ in India.
- 11665-1985
- 11664-1984
- 11669-1986
- None of these
Q9: Sectional area is shown by hatching lines which are generally inclined at –
- 450
- 300
- 600
- 750
Q10: Size ‘D1’ of the drawing board refers to _______ (l x w x t) mm.
- 1500 x 1000 x 25
- 1000 x 700 x 25
- 700 x 500 x 15
- 500 x 350 x 15
Q11: In inclined lettering, the stem is inclined _____ to the left.
- 150
- 350
- 450
- 750
Q12: As per recommendations of IS: 11665-1985, the LHS side margin line of a drawing sheet for class work should be kept as _____ mm
- 5 mm
- 10 mm
- 15 mm
- 20 mm
Q13: ______ is generally used to show areas of sections.
- Hatching
- Shading
- Dimensioning
- None of these
Q14: The section lines are equally spaced ________ lines.
- Thick
- Thin
- Medium
- Dotted
Q15: The Top, Front and Bottom views align in this manner ______.
- Horizontally
- Vertically
- According to the planed views
- Parallel to the frontal planes
Q16: For orthographic projection, the engineering custom bureau of Indian Standards dictates the use of:
- First-angle projection
- Second-angle projection
- Third-angle projection
- Fourth-angle projection
Q17: Hatching lines are drawn at an angle of ______.
- 150
- 300
- 450
- 600
Q18: In an isometric sketch of a cube
- The receding axes are at 45 degree to the horizontal
- the frontal face appears in its true shape
- only the depth distances must be reduced
- all faces are equally distorted
Q19: Super imposed dimensioning is the simplest method of _______.
- Chain dimensioning
- Parallel dimensioning
- Combined dimensioning
- Tabular dimensioning
Q20: When (1) visible outlines (2) hidden outlines (3) projection lines and (4) centre lines overlap, the recommended sequence of priority is
- 1-2-3-4
- 1-2-4-3
- 2-1-3-4
- 2-1-4-3
Q21: Which of the following publications made by Bureau of Indian Standards includes standard techniques for line conventions and lettering in detail?
- SP 46
- BIS 9609
- ASME Y 14.2M
- ISO 2009
Q22: The projection showing the front in the true shape and size is
- isometric
- perspective
- oblique
- axonometric
Q23: Which is not a principal view?
- front
- bottom
- auxiliary
- left side
Q24: This type of projection is when projectors are parallel to each other, but are at an angle other than 90 degrees to the plane of projection:
- perspective
- oblique
- aesthetic
- angular
Q25: This is how axonometric, oblique, and perspective sketches show objects
- Orthographically
- Pictorially
- Obliquely
- Parallel
Q26: The solid having a polygon for a base and triangular lateral faces intersecting at a vertex is
- pyramid
- prism
- cone
- torus
Q27: This type of section is limited by a break line
- removed section
- revolved section
- broken-out section
- half section
Q28: This type of section is not in direct projection from the view containing the cutting plane
- removed section
- revolved section
- broken-out section
- full section
Q29: The curve generated by a point on the circumference of a circle, which rolls without slipping along outside of another circle is known as
- Hypocycloid
- Epicycloid
- Cycloid
- Trochoid
Q30: In orthographic projections, the rays are assumed to
- diverge from station point
- converge from station point
- be parallel
- None of these
Q31: Which of the following object gives a circular section, when it is cut completely by a section plane (irrespective of the angle of the section plane)
- Cylinder
- Sphere
- Cone
- Circular lamina
Q32: Comparative scale is a pair of scale having a common
- units
- representative fraction
- length of scale
- least count
Q33: An angle can be set off and measured with the help of
- plane scale
- diagonal scale
- comparative scale
- Scale of chords
Q34: Which types of line is used to draw dimension lines?
- Long chain thin
- Long chain thick
- Continuous thin
- Continuous thick
Q35: Dimensions giving close to each other and in a straight is called
- Chain dimensioning
- Parallel dimensioning
- Combine dimensioning
- None of the above
Q36: Two recommended systems of placing the dimensions are
- Unidirectional and aligned
- Upright and inclined systems
- Linear and oblique systems
- Linear and inclined systems
Q37: Grid References on a drawing sheet provide the following information
- Location of details, additions, modifications, revisions, etc. of drawing
- To facilitate the positioning of the drawing when reproduced
- To facilitate trimming
- To facilitate brief record and initials of the person responsible
Q38: Revision tables on a drawing sheet provide the following information
- Designation of revision
- Date of revision
- Initials of the person responsible
- All the above
Q39: Center lines are used to locate or represent the centers of .
- Arcs
- Circles
- Hidden round features
- All of the above
Q40: Dimension line should not _____to each other
- Parallel
- Cross
- Perpendicular
- Inclined
Q41: The part that doesn’t belong to T-square is __________
- Working edge
- Blade
- Stock
- Ebony edge
Q42: The stock and the blade of the T-square are joined at ______ to each other.
- 45°
- 30°
- 60°
- 90°
Q43: Which of the following tools is used to draw horizontal lines?
- Mini – drafter
- Protractor
- T – square
- French curve
Q44: Which of the following instrument can be used to draw accurate perpendicular lines, parallel lines and angular lines?
- Mini – drafter
- T – square
- Protractor
- Set square
Q45: Which is the most common drawing tool used to draw circles?
- French curve
- Mini – drafter
- Divider
- Compass
Q46: The angle which we can’t make using a single Set-square is ________
- 45°
- 60°
- 30°
- 75°
Q47: Using 30° – 60° – 90° and 45° – 45° – 90° set squares, which of the following angle is not possible to draw?
- 45°
- 30°
- 10°
- 90°
Q48: Which is the instrument used to draw parallel lines fast?
- Set square
- Ruler scale
- Protractor
- Roll-n-draw ruler
Q49: Which of the following cannot be drawn accurately using roll-n-draw RULER?
- Lines
- Horizontal lines
- Parallel lines
- Continuous curves
Q50: Small bow compass can draw circles less than _____ mm radius.
- 25mm
- 30mm
- 35mm
- 40mm
Q51: Continuous thin, line are used for _________.
- Hidden outlines
- Cutting planes
- Centre lines
- Dimension lines
Q52: The line given below is used for_______.
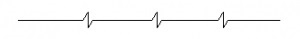
- Long-break line
- Cutting plane
- Centroidal lines
- Out lines of adjacent parts
Q53: The line given below is used for_______.
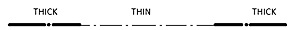
- Hidden outlines
- Cutting planes
- Hidden edges
- Dimension lines
Q54: The line given below is used for_______.
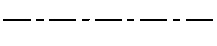
- Long-break line
- Cutting plane
- Centre lines
- Out lines of adjacent parts
Q55: Which line is used for drawing visible outlines and visible edges?
- Long-break line
- Dashed thick
- Continuous thick line
- Chain thick
Q56: Which of the following lines are used to show that the object is cut and then viewed?
- Hidden lines
- Leader lines
- Centre lines
- Hatching Lines
Q57: From the below figure, what is the name of the line X?
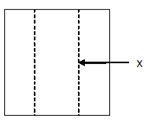
- Outline
- Section line
- Hidden line
- Hatching
Q58: What is the type of line used for line “a”?
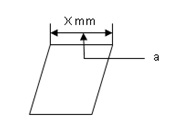
- Continuous thick
- Continuous thin straight
- Medium thick short dashes
- Chain thin
Q59: The axis of the cylinder or sphere is denoted by which of the following line?
- Section line
- Centre line
- Hidden line
- Leader line
Q60: What is the standard length and width of the arrowhead of dimension lines?
- 2mm and 2mm
- 3mm and 1mm
- 4mm and 2mm
- 3mm and 2mm
Q61: How many pairs of parallel lines are there in a regular pentagon?
- 0
- 1
- 2
- 5
Q62: Sum of the four angles in a quadrilateral is (interior angles) equal to ________
- 180°
- 90°
- 360°
- 120°
Q63: What is the length of the short dashes of the centre lines?
- 5mm
- 2mm
- 1mm
- 3mm
Q64: Which type of line is used to join the dimension line and the curve that needs to be dimensioned?
- Leader line
- Outline
- Dimension line
- Section line
Q65: How many pairs of parallel lines are there in regular Hexagon?
- 2
- 3
- 6
- 1
Q66: Which of the following is not a type of quadrilateral?
- Rectangle
- Square
- Rhomboid / Parallelogram
- Circle
Q67: In a square how many angles are at right angles.
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
Q68: If an angle which is less than 90⁰ is called an
- Right angle
- Obtuse angle
- Straight angle
- Acute angle
Q69: If an angle which is more than 90⁰ is called an
- Right angle
- Obtuse angle
- Straight angle
- Acute angle
Q70: When the sum of the two adjacent angles is equal to 180⁰, are called
- Supplementary angles
- Obtuse angle
- Straight angle
- Acute angle
Q71: Sum of the three angles in a triangle is (interior angles) equal to
- 180⁰
- 90⁰
- 360⁰
- 120⁰
Q72: ________ is a triangle having all the three sides equal.
- Isosceles triangle
- Scalene triangle
- Equilateral triangle
- Right angled triangle
Q73: The side opposite to right angle in Right angled triangle is called
- Adjacent side
- Hypotenuse
- Opposite side
- Line
Q74: In a ________ opposite sides are equal and parallel. Opposite angles are also equal.
- Rectangle
- Square
- Parallelogram
- Circle
Q75: The distance from the centre to any point on the Circle is called the
- Circumference
- Radius
- Diameter
- Segment
Q76: When two or more circles having common centre, they are called
- Concentric circles
- Circles
- Eccentric circles
- Triangle
Q77: Circles within a circle but with different centres are called
- Concentric circles
- Circles
- Eccentric circles
- Triangle
Q78: A part of the circle between any two points on the circumference or periphery is called an
- Circumference
- Radius
- Diameter
- Arc
Q79: ________ is a plane figure bounded by usually five or more straight lines.
- Polygon
- Circle
- Triangle
- Rectangle
Q80: The sum of exterior angles of a polygon is equal to
- 180⁰
- 90⁰
- 360⁰
- 120⁰
Q81: The sum of the interior angle and the corresponding external angle is
- 180⁰
- 90⁰
- 360⁰
- 120⁰
Q82: What is the name of polygon having eight side?
- Pentagon
- Hexagon
- Octagon
- Heptagon
Q83: Identify the style of given lettering:
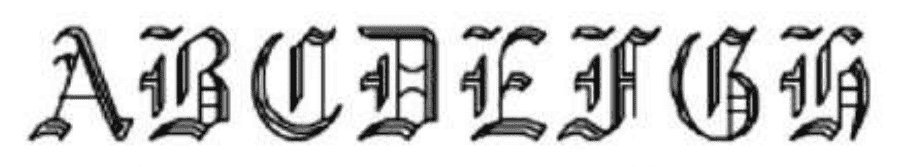
- Uppercase Italic
- Uppercase Gothic
- Uppercase Text
- Uppercase Roman
Q84: The standard heights recommended by BIS SP: 46-2003 are in the progressive ratio of
- square root 3
- Square root 4
- Square root 2
- Square root 5
Q85: What is the name of line mark as "X" in single stroke lettering?
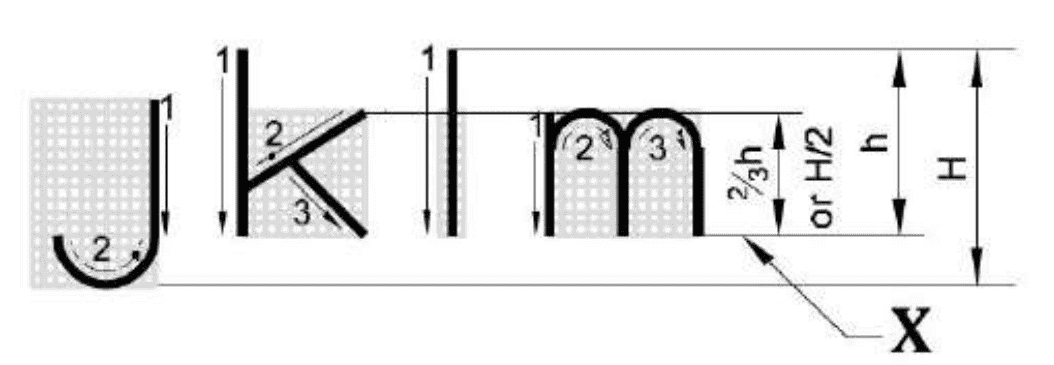
- Waist Line
- Cap Line
- Drop Line
- Base Line
Q86: What is the name of line mark as "X" in single stroke lettering?
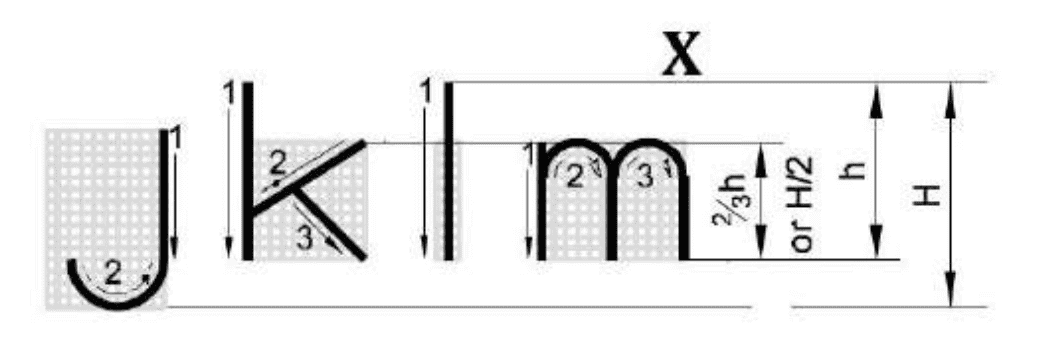
- Waist Line
- Cap Line
- Drop Line
- Base Line
Q87: What is the angle of inclination from horizontal in Italic Lettering?
- 15⁰
- 30⁰
- 75⁰
- 45⁰
Q88: What is the angle of inclination towards right in Italic Lettering?
- 15⁰
- 30⁰
- 75⁰
- 45⁰
Q89: If all the angles of a triangle are acute, the triangle is known as?
- Equiangular triangle
- Acute angled triangle
- Obtuse angled triangle
- Right angled triangle
Q90: How many line segments are there in a quadrilateral?
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
Q91: Which one of the following is a quadrilateral?
- Rectangle
- Equilateral triangle
- Line
- All of these
Q93: The angle which is equal to 90⁰ is classified as
- Acute angle
- Obtuse angle
- Right angle
- Reflex angle
Q94: At least two sides are the same length called as
- Obtuse Triangle
- Right Triangle
- Isosceles Triangle
- Scalene Triangle
Q95: There are two pairs of parallel sides. Opposite sides are the same length.
- Rhombus
- Polygon
- Parallelogram
- Trapezoid
Q96: All sides are the same length. Opposite sides are parallel. There are 4 right angles.
- Rectangle
- Trapezoid
- Quadrilateral
- Square
Q97: To construct a square, we need to know:
- All the interior angles
- All the side lengths
- Only one interior angle
- Only one side length
Q98: To construct a rectangle, we need to know:
- All the interior angles
- All the Sides
- Only Length and breadth
- Only one angle measure
Q99: A triangle in which two sides are equal is called _____.
- Scalene triangle
- Equilateral triangle
- Isosceles triangle
- None of the above
Q100: The angles opposite to equal sides of a triangle are _____.
- Equal
- Unequal
- Supplementary angles
- Complementary angles
Q101: The center of the circle lies in _____ of the circle.
- Interior
- Exterior
- Circumference
- None of the above
Q102: The number of tangents that can be drawn to a circle from a point outside is:
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
Q103: Identify the style of given lettering:
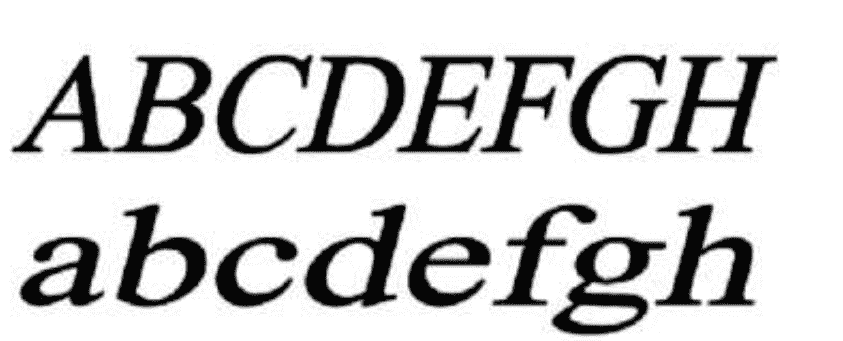
- Gothic
- Roman
- Italic
- Text
Q104: Identify the style of given lettering:

- Gothic
- Roman
- Italic
- Text
Q105: Identify the style of given lettering:

- Gothic
- Roman
- Italic
- Text
Q106: Identify the style of given lettering:

- Lowercase Gothic
- Lowercase Roman
- Uppercase Gothic
- Uppercase Roman
Found a mistake or mismatch in the question or answer? Let us know via email.
This post is licensed under CC BY 4.0 by the author.