Wiring Installation and Earthing
Electrician Trade Theory, Module-9
Wiring Installation and Earthing
⭕️ Show all Answers
Q1: What is the minimum size of copper earth continuity conductor used in single phase domestic wiring as per BIS?
- 3 Sq.mm
- 3.5 Sq.mm
- 2.5 Sq.mm
- 1.5 Sq.mm
Q2: Which method is used to reduce earth resistance value in a existing earth?
- Increasing the length of electrode
- Keeping wet condition in earth pits always
- Adding more sand and charcoal in earth pits
- Increasing the diameter of earth electrode
Q3: Why A.C is required to measure the earth resistance by using earth resistance tester?
- Regulate the current
- Increase the voltage drop
- Decrease the voltage drop
- Avoid electrolytic emf interference
Q4: What is the formula to find voltage drop of a AC single phase wiring circuit?
- Voltage drop = IR volt
- Voltage drop = I²R volt
- Voltage drop = I/R volt
- Voltage drop = IR/2 volt
Q5: What is the maximum permissible load for a power sub circuit as per I.E rules?
- 800 Watt
- 1500 Watt
- 2000 Watt
- 3000 Watt
Q6: Which location the service connection supply leads to be connected at consumer main board?
- IC cut out
- Main switch
- Energy meter
- Distribution board
Q7: What is the type of test in domestic wiring installation?
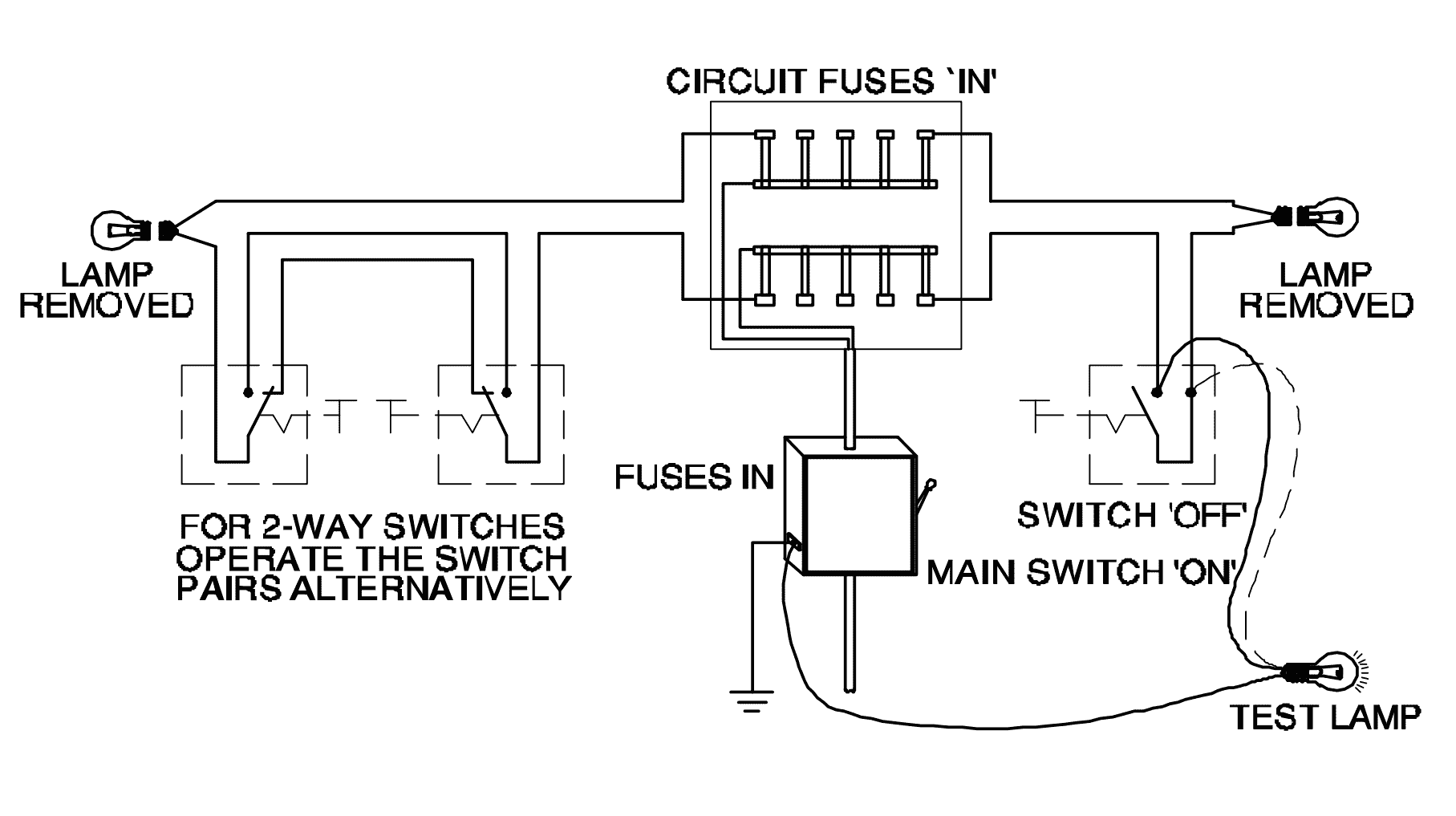
- Polarity test
- Continuity (or) open circuit test
- Insulation resistance test between conductors
- Insulation resistance test between conductors and earth
Q8: What is the permissible leakage current in domestic wiring installation?
- 1/5 x Full load current
- 1/50 x Full load current
- 1/500 x Full load current
- 1/5000 x Full load current
Q9: Which instrument is used to test new domestic wiring installation?
- Multimeter
- Megger
- Shunt type ohmmeter
- Series type ohmmeter
Q10: What is the type of test in the wiring installation?
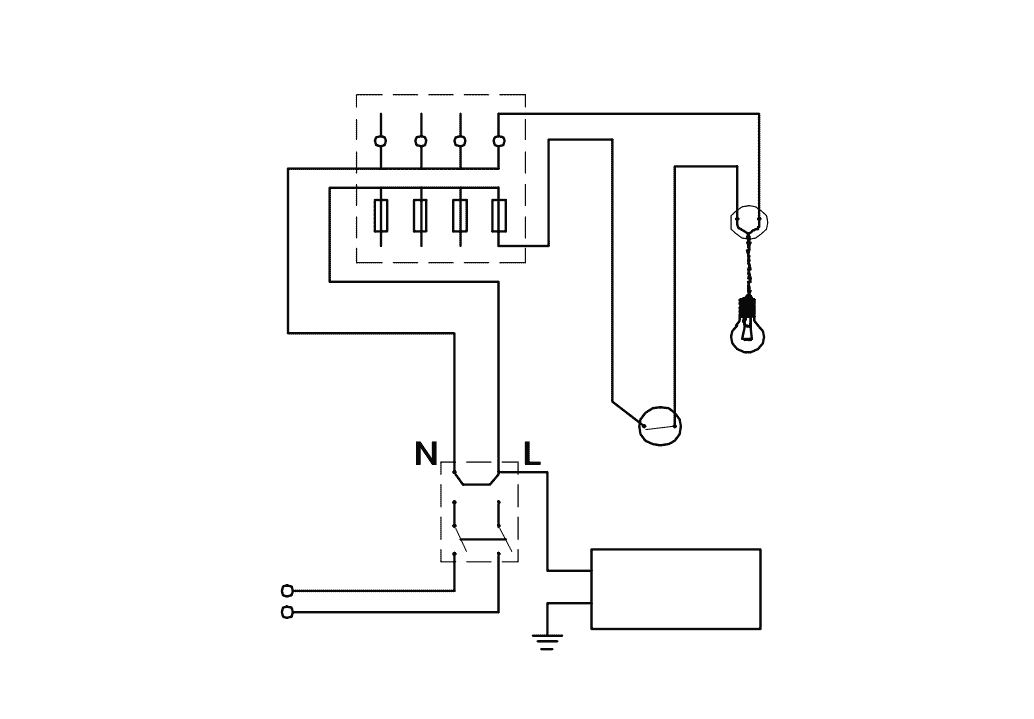
- Polarity test
- Open circuit test
- Insulation resistance test between conductors
- Insulation resistance test between conductors and earth
Q11: Where system earthing is done?
- Generating station
- Electroplating installation
- Small industrial installation
- Domestic wiring installation
Q12: What is the test to be carried out by using megger?
- Polarity test
- Insulation resistance test
- Earth electrode resistance test
- Earth conductor continuity test
Q13: What is the reason of lamp glowing dim and motor running slow in a domestic wiring circuit?
- Open circuit in the neutral line
- Short circuit between conductors
- High value series resistance fault
- Open circuit in the earth conductor
Q14: Which wiring installation the System earthing is to be done?
- Substations
- Godown wiring
- Domestic wiring
- Commercial wiring
Q15: Which method of earth resistance measurement is illustrated?
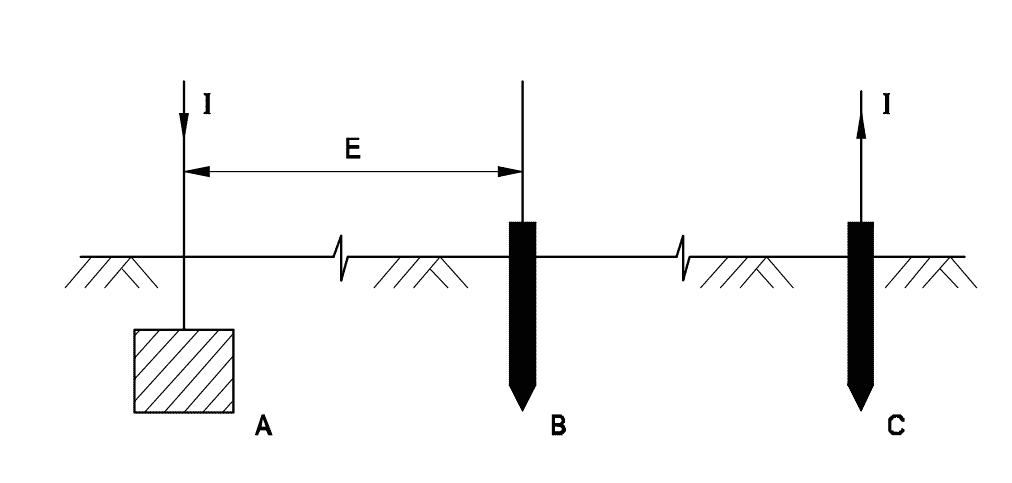
- Fall of current
- Fall of potential
- Current dividing
- Potential dividing
Q16: How to control harmonic distortions in neutral connections as per IE rule?
- Earthing through impedance
- Providing by plate earthing
- Increasing conductor size
- Providing parallel earthing
Q17: What is the function of current reverser in earth resistance tester?
- Converts A.C. into D.C
- Reverses the polarity of D.C
- Changes D.C. supply into A.C supply
- Reverses the direction of rotation of the generator
Q18: What is the advantage of stranded conductor over solid conductor?
- Cost is less
- More flexible
- Less voltage drop
- More insulation resistance
Q19: How the earth resistance can be reduced?
- Providing double earthing
- Reducing the pit depth for earthing
- Increasing the length of the electrodes
- Decreasing the length of the electrodes
Q20: What is the reason for supplying AC to the electrodes for measuring earth resistance?
- Provide electrostatic shield
- Protect the cojis in the meter
- Reduce the value of current in the meter
- Avoid the effect of electrolytic emf interference
Q21: Why the pointer is not stable at zero on the scale as the megger is not in use?
- It is not having controlling Torque
- Provided with air friction damping
- The deflecting torque is directly proportional to the current
- The deflecting torque is directly proportional to the square of the current
Q22: Which is proportional for the deflection of ohmmeter needle in earth resistance tester?
- Current in current coil
- Current in potential call
- Speed of the handle rotation
- Ratio of the current in two coils
Q23: Which principle the earth resistance tester works?
- Self induction
- Mutual induction
- Fall of potential method
- Fleming's left hand rule
Q24: Why system earthing is different in utilization than equipment earthing?
- It protects human only
- it protects from all circuit faults
- It is associated with current carrying conductors
- it is connected to the non current carrying metal work
Q25: What is the effect if a person receives a shock current of 20 mA?
- No sensation
- Painful shock
- Heart convulsions
- Become unconscious
Q26: Which electrical equipment L' series type MCB's are used?
- Geysers
- Locomotives
- Halogen lamps
- Air conditioners
Q27: What is the megger reading in a dead short wiring installation?
- 0 MΩ
- 1 MΩ
- 500 MΩ
- Infinity
Q28: What is the advantage of crimping?
- Gives neat appearance
- Reduce load current
- Avoid loose connections
- Easy to replace
Found a mistake or mismatch in the question or answer? Let us know via email.
This post is licensed under CC BY 4.0 by the author.
