Basic Electrical Practice
Electrician Trade Theory, Module-4
Basic Electrical Practice
⭕️ Show all Answers
Q1: How many electrons are there in the third cell of the copper atom?
- 8
- 13
- 18
- 29
Q2: Which is the semiconductor material?
- Eureka
- Ebonite
- Manganin
- Germanium
Q3: What is the indication of neon polarity indicator used for checking A.C. supply?
- Both electrodes will glow
- Only one electrode will glow
- Both electrodes will be flickering
- One electrode will glow and another will be flickering
Q4: Calculate the electrical energy in unit consumed by 500W lamp for 5 hours.
- 0.5 unit
- 1.0 unit
- 1.5 unit
- 2.5 unit
Show Calculation
\[ \text{Energy} = \frac{500 \times 5}{1000} = 2.5 \text{ units} \]Q5: What is the value of hot resistance of a bulb rated as 100W/250V?
- 31.25 ohm
- 62.50 ohm
- 312.50 ohm
- 625.00 ohm
Show Calculation
\[ R = \frac{V^2}{P} = \frac{250^2}{100} = \frac{62500}{100} = 625\,\Omega \]Q6: Which law states that in closed electric circuit, the applied voltage is equal to the sum of the voltage drops?
- Ohm’s law
- Laws of resistance
- Kirchhoff’s first law
- Kirchhoff’s second law
Q7: Calculate the total power of the circuit of two lamps rated as 200W/240V are connected in series across 240V supply?
- 100 W
- 50 W
- 200 W
- 400 W
Show Calculation
\[ R = \frac{V^2}{P} = \frac{240^2}{200} = 288\,\Omega \quad \text{(per lamp)} \]\[ \text{Total resistance} = 576\,\Omega \]\[ I = \frac{240}{576} = 0.416\,\text{A} \]\[ P = I^2 \times R = (0.416)^2 \times 576 \approx 100\,W \]Q8: What is the formula for the equivalent resistance (RT) of the three resistors R1, R2 & R3 connected in parallel circuit?
- \(R_T = R_1 + R_2 + R_3\)
- \(R_T = \frac{R_1 R_2 R_3}{R_1 + R_2 + R_3}\)
- \(R_T = \frac{R_1 + R_2 + R_3}{3}\)
- \(\frac{1}{R_T} = \frac{1}{R_1} + \frac{1}{R_2} + \frac{1}{R_3}\)
Q9: What is the reading of ohmmeter across opened ‘R2’ resistor?
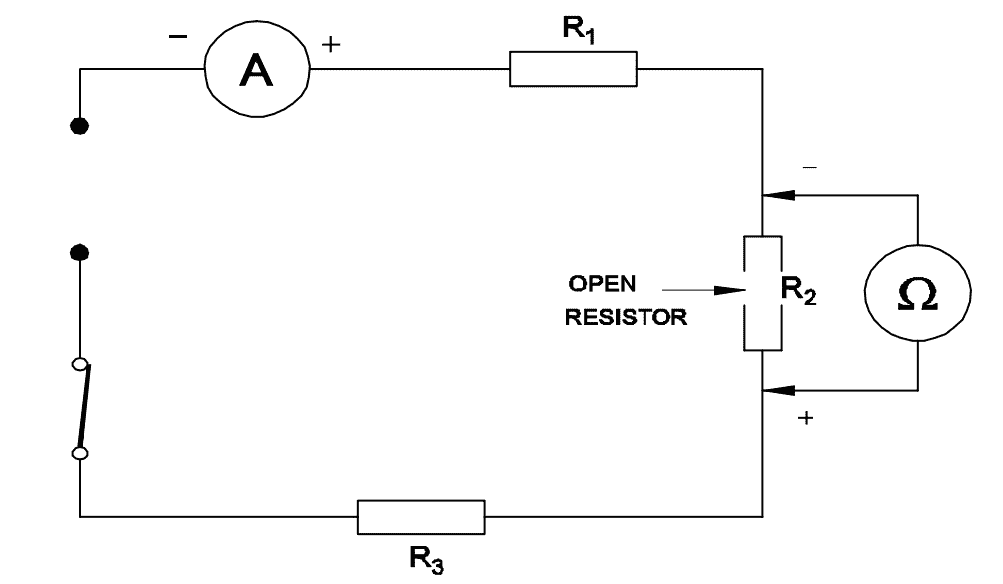
- Indicate zero reading
- Indicate infinite resistance
- Total resistance value of the circuit
- Value of sum of the resistance of R1 and R3 only
Q10: What is the change of resistance value of the conductor as its diameter is doubled?
- Increases to two times
- Decreases to four times
- Decrease to half of the value
- No change in value of resistance
Show Calculation
\[ R \propto \frac{1}{A} \quad \text{and} \quad A \propto d^2 ~ \text{If } d \rightarrow 2d, \] \[ \text{ then } A \rightarrow 4A \Rightarrow R \rightarrow \frac{R}{4} \]Q11: What is the name of the resistor?
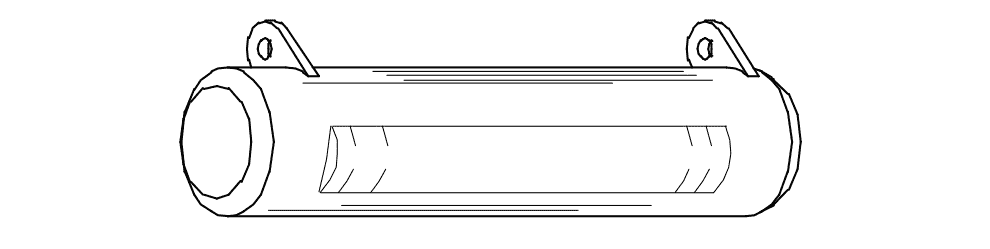
- Metal film resistor
- Wire wound resistor
- Carbon – film resistor
- Carbon composition resistor
Q12: Calculate the resistance value of the resistor by colour coding method.
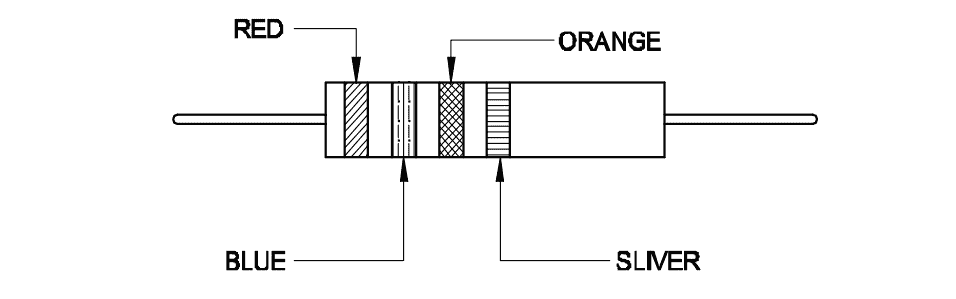
- \(23 \times 10^3\,\Omega \pm 5\%\)
- \(26 \times 10^3\,\Omega \pm 10\%\)
- \(32 \times 10^4\,\Omega \pm 10\%\)
- \(37 \times 10^4\,\Omega \pm 5\%\)
Show Resistance Calculator
Q13: Why the ohmmeter is graduated with non-linear scale?

- Voltage is directly proportional to resistance
- Current is inversely proportional to resistance
- Resistance is inversely proportional to the square of current
- Voltage is directly proportional to the square of the current
Q14: Calculate the value of unknown resistance ‘RDC’ in the Wheatstone bridge network, if PAB = 500 Ω, QBC = 300 Ω, SAD = 15 Ω at balanced condition.
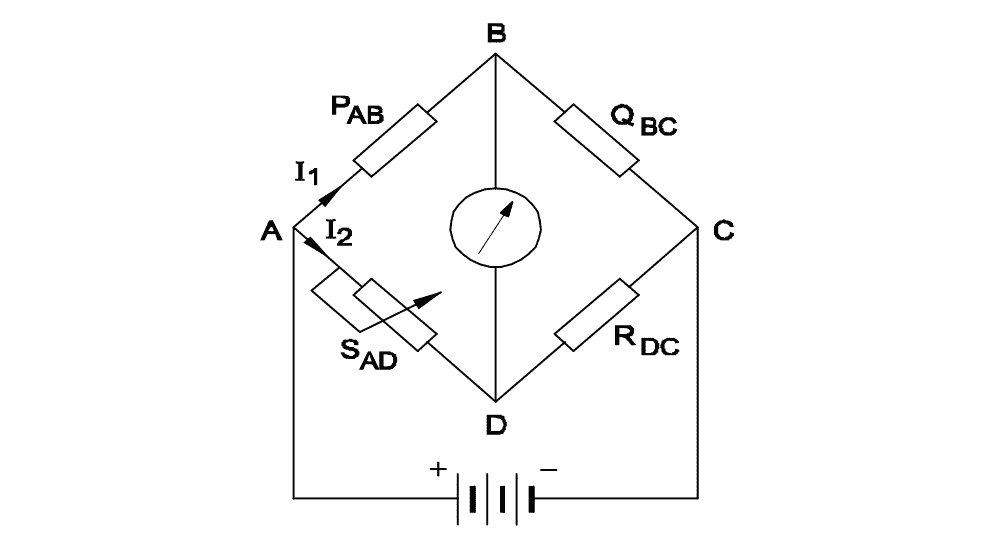
- 12 Ω
- 9 Ω
- 6 Ω
- 3 Ω
Show Calculation
\[ R_{DC} = \frac{Q_{BC} \times S_{AD}}{P_{AB}} = \frac{300 \times 15}{500} = 9\,\Omega \]Q15: Which material is having negative temperature co-efficient property?
- Mica
- Eureka
- Copper
- Manganin
Q16: What electrical quantities are related in Ohm’s law?
- Current, resistance and power
- Current, voltage and resistivity
- Current, voltage and resistance
- Voltage, resistance and current density
Q17: Calculate the value of resistance R2 in the parallel circuit.
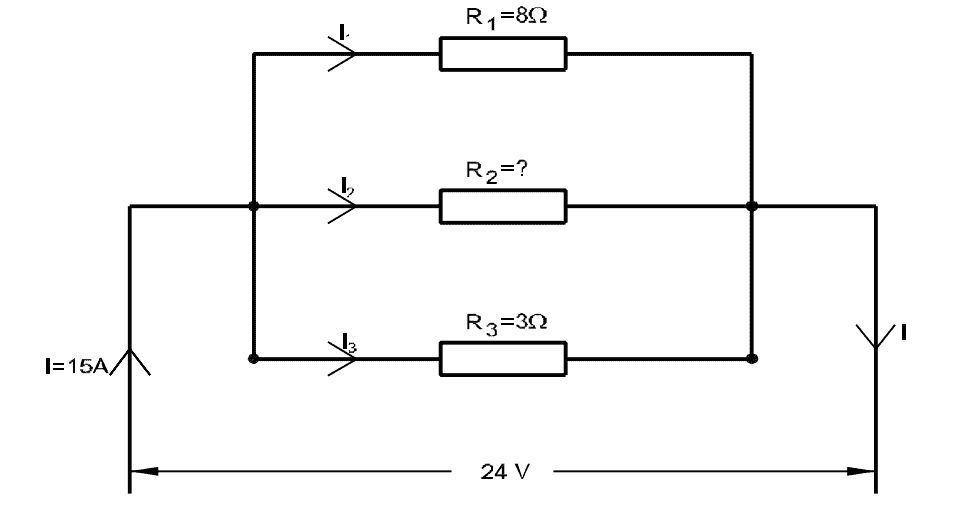
- 2 Ω
- 4 Ω
- 6 Ω
- 8 Ω
Show Calculation
\[I_1 = \frac{24}{8} = 3\,\text{A}, \quad I_3 = \frac{24}{3} = 8\,\text{A}\]
\(I_2 = 15 - 3 - 8 = 4\,\text{A}\)
\(R_2 = \frac{24}{4} = \boxed{6\,\Omega}\)
Q18: What is the effect of the parallel circuit with one branch opened?
- Current will remain same
- Whole circuit will not function
- No current will flow in that branch
- Voltage drop increase in the opened branch
Q19: What is the unit of resistivity?
- ohm / cm
- ohm / cm²
- ohm · metre
- ohm / metre
Q20: Which type of resistor is used for Arc quenching protection in circuit breakers?
- Varistors
- Sensistors
- Thermistors
- Light dependent resistor (LDR)
Q21: Calculate the value of resistance by colour coding method.
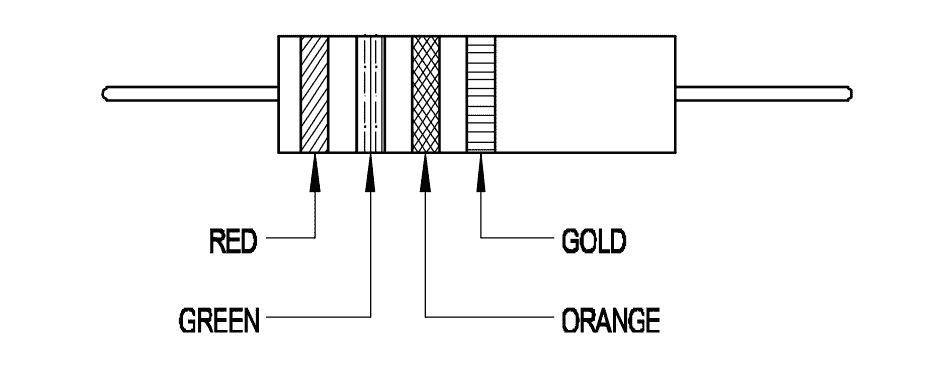
- \(22 \times 10^3\,\Omega \pm 10\%\)
- \(23 \times 10^4\,\Omega \pm 10\%\)
- \(25 \times 10^3\,\Omega \pm 5\%\)
- \(36 \times 10^4\,\Omega \pm 5\%\)
Show Resistance Calculator
Q22: Calculate the unknown resistance “RDC” in the Wheatstone bridge circuit, if \(P_{AB}=400\,\Omega\), \(Q_{BC}=200\,\Omega\) and \(S_{AD}=12\,\Omega\) at balanced condition.
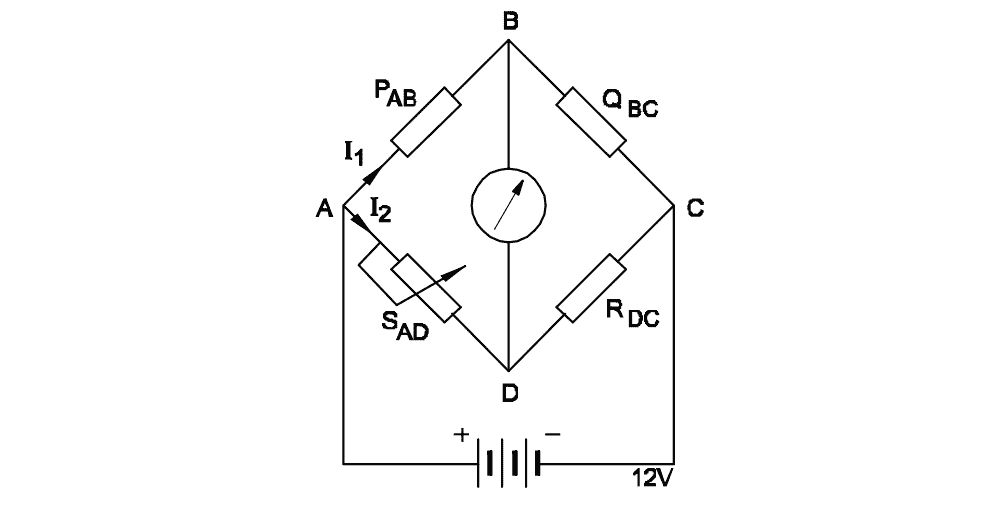
- 4 Ω
- 6 Ω
- 8 Ω
- 12 Ω
Show Calculation
Using: \[ \frac{P_{AB}}{Q_{BC}} = \frac{S_{AD}}{R_{DC}} \]\[ \Rightarrow R_{DC} = \frac{Q_{BC} \times S_{AD}}{P_{AB}} = \frac{200 \times 12}{400} = 6\,\Omega\]Q23: What is the reading of the voltmeter ‘V’?
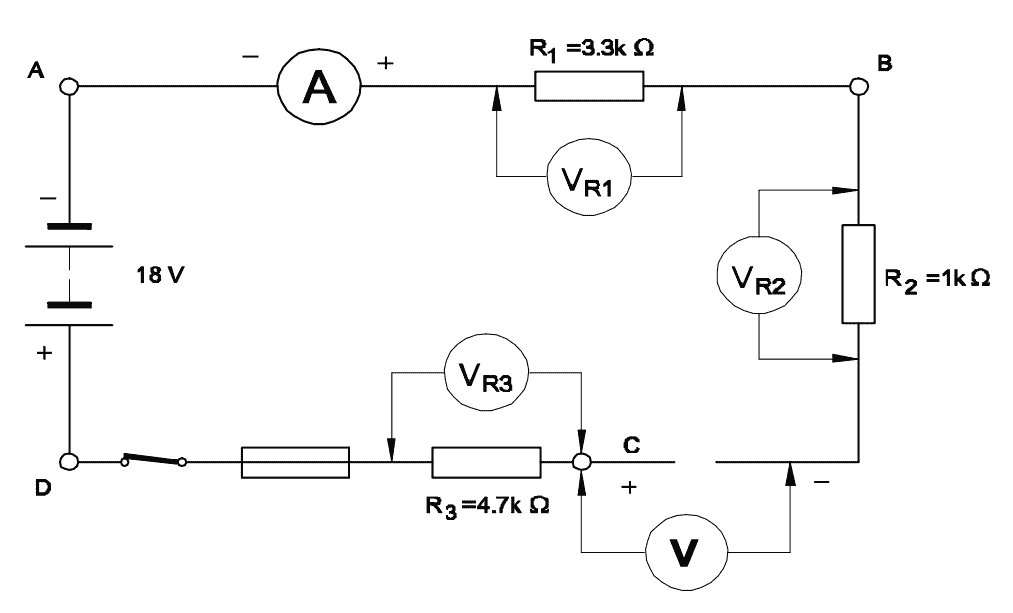
- 0 V
- 6 V
- 9 V
- 18 V
Q24: Which is the application of series circuit?
- Voltmeter connection
- Lighting circuits in home
- Shunt resistor in ammeter
- Multiplier resistor of a voltmeter
Q25: What is the effect on opened resistor in series circuit?
- No effect in opened resistor
- Full circuit current will flow in opened resistor
- Total supply voltage will appear across the opened resistor
- No voltage will appear across the opened resistor
Q26: Calculate the resistance value in R3 resistor.
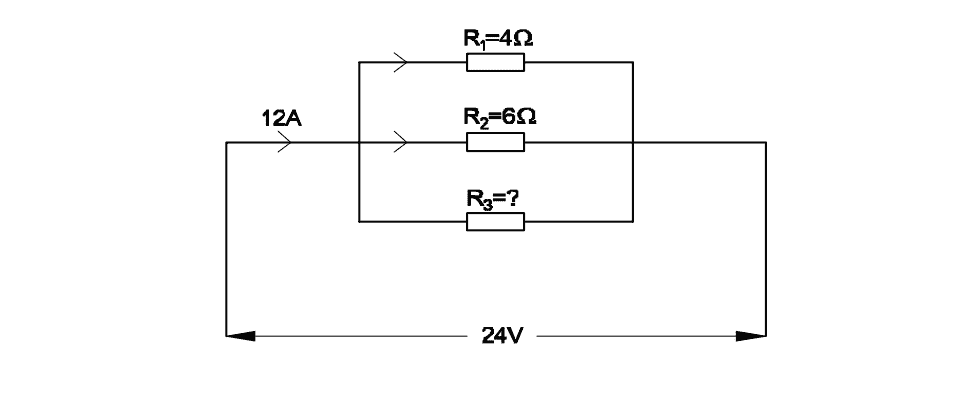
- 4 Ω
- 6 Ω
- 8 Ω
- 12 Ω
Show Calculation
\[ R_{total} = \frac{V}{I} = \frac{24}{12} = 2\,\Omega \] For resistors in parallel: \[ \frac{1}{R_{total}} = \frac{1}{R_1} + \frac{1}{R_2} + \frac{1}{R_3} \] \[\Rightarrow \frac{1}{2} = \frac{1}{4} + \frac{1}{6} + \frac{1}{R_3} \] \[ \Rightarrow \frac{1}{2} - \frac{1}{4} - \frac{1}{6} = \frac{1}{R_3} \] \[ \Rightarrow \frac{6 - 3 - 2}{12} = \frac{1}{R_3} \] \[ \Rightarrow \frac{1}{R_3} = \frac{1}{12} \] \[ \Rightarrow R_3 = 12\,\Omega \]Q27: What is the effect of the circuit, if ‘ab’ points are shorted?
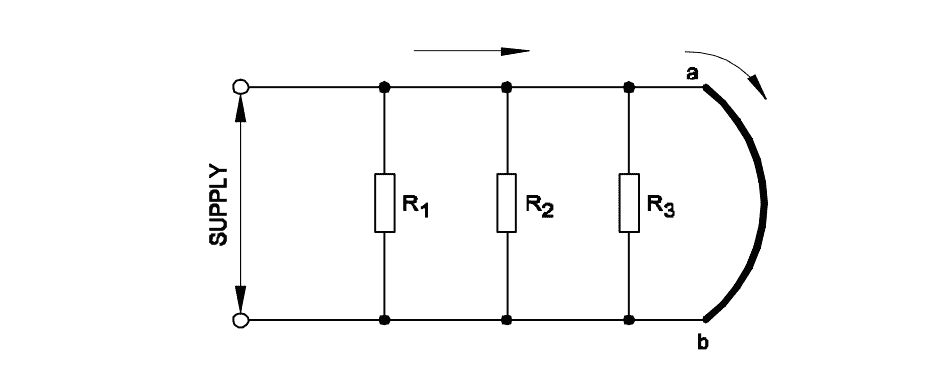
- Circuit resistance will be zero
- Same current will flow in all branches
- Supply voltage will exist in each branch
- Total circuit current is equal to each branch circuit current
Q28: What is the name of the resistor if its resistance value increases with increase in temperature?
- Varistors
- Sensistors
- Thermistors
- Light Dependent Resistor (LDR)
Q29: What is the formula for Quantity of electricity (Q)?
- Current × Time
- Voltage × Current
- Current × Resistance
- Voltage × Resistance
Show Explanation
\(Q = I \times t\)Q30: What is the unit of conductance?
- Mho
- Ohm
- Ohm-m
- Ohm/m
Q31: Which one defines the change in resistance in Ohm (Ω) per degree centigrade (°C)?
- Temperature effect
- Laws of temperature
- Temperature constant
- Temperature co-efficient
Q32: Which type of meter is used to test the polarity of battery?
- Moving iron ammeter
- Moving coil voltmeter
- Moving iron voltmeter
- Dynamo meter type wattmeter
Q33: What is the voltage drop in resistor ‘R2’ in the series circuit?
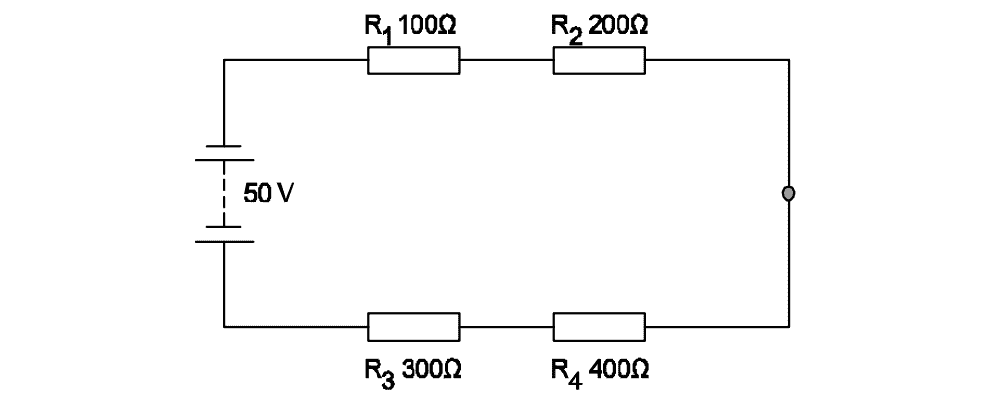
- 5 Volt
- 10 Volt
- 15 Volt
- 20 Volt
Show Calculation
\[I = \frac{V_{\text{total}}}{R_{\text{total}}} = \frac{50\,\text{V}}{1000\,\Omega} = 0.05\,\text{A}\] \[V_{R_2} = I \times R_2 = 0.05\,\text{A} \times 200\,\Omega = 10\,\text{V}\]Q34: Which is the application of series circuit?
- Fuse in circuit
- Voltmeter connection
- Electrical lamp in homes
- Shunt resistor in ammeter
Q35: Which method is used for measuring 1 Ohm to 100K Ohm range resistance?
- Substitution method
- Kelvin bridge method
- Wheat stone bridge method
- Voltmeter and ammeter method
Q36: What is the S.I unit of specific resistance?
- \(\Omega/\text{cm}\)
- \(\Omega/\text{metre}^2\)
- \(\Omega\cdot\text{metre}\)
- \(Micro ohm/cm²\)
Q37: What is the value of resistance of the resistor?
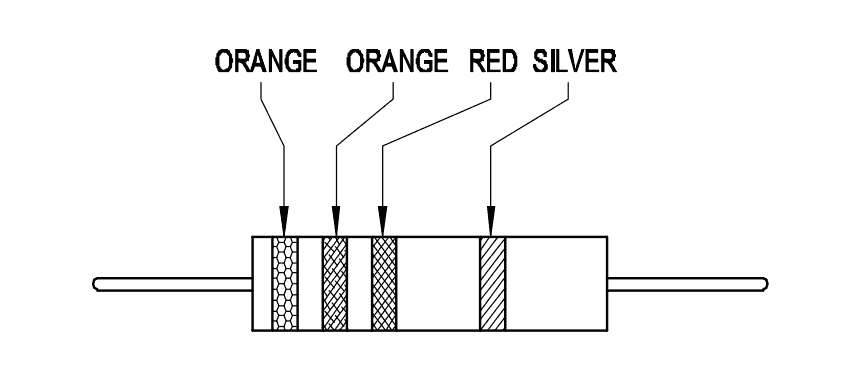
- 330 ± 5% Ohm
- 3300 ± 10% Ohm
- 33000 ± 5% Ohm
- 330000 ± 10% Ohm
Show Resistance Calculator
Q38: What is the purpose of the shunt resistor ‘R2’ used in series type Ohm meter circuit?
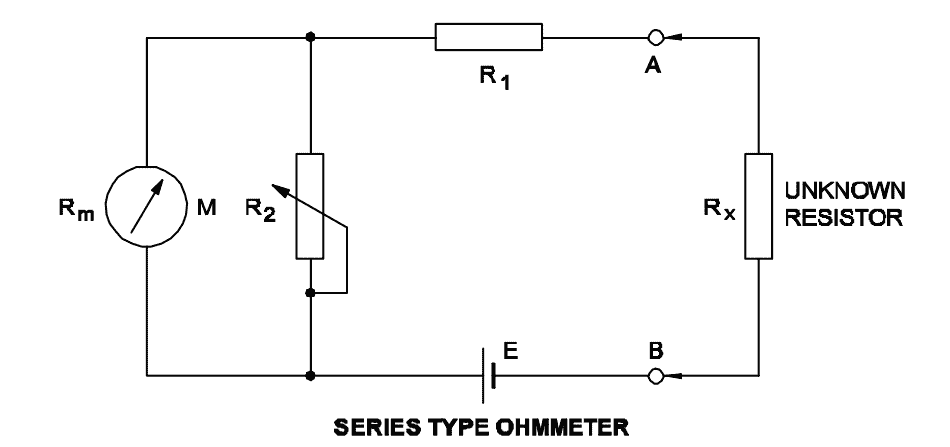
- To limit the current in the circuit
- To increase the value of meter resistance
- To adjust the zero position of the pointer
- To prevent the excess current in the circuit
Q39: Which electrical quantity affects the heat generated in a conductor?
- Voltage
- Square of the current
- Square of the resistance
- Current passed through it
Show Explanation
\[Joule's Law: H \propto I^2 R t \]Q40: What is the change in value of resistance of the conductor, if its cross section area is doubled?
- No change
- Decreases 2 times
- Increases 2 times
- Decreases 4 times
Show Calculation
\[Since~ R \propto \frac{1}{A}\]\[ doubling~ A \Rightarrow R ~becomes~half \]Q41: Calculate the voltage drop across the resistor ‘R4’ in the circuit.
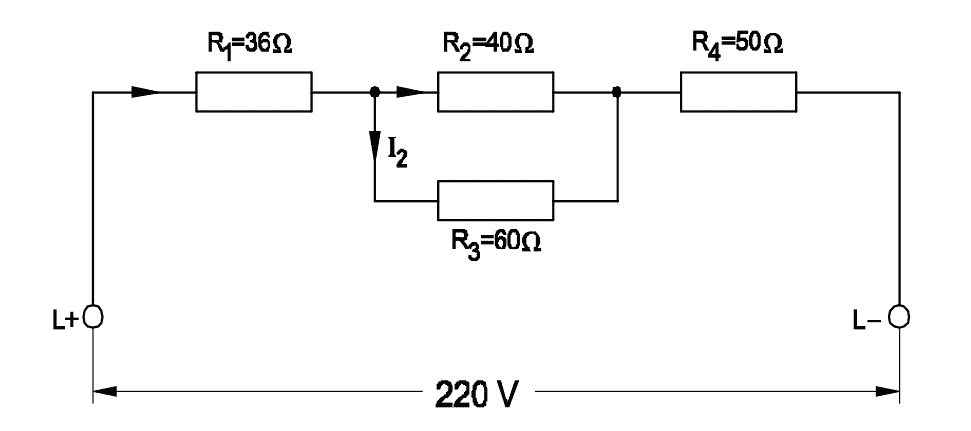
- 48 V
- 72 V
- 80 V
- 100 V
Show Calculation
\[\frac{1}{R_{23}} = \frac{1}{R_2} + \frac{1}{R_3} = \frac{1}{40} + \frac{1}{60}\] \[\frac{1}{R_{23}} = \frac{3 + 2}{120} = \frac{5}{120} = \frac{1}{24} \Rightarrow R_{23} = 24\,\Omega\] \[R_{\text{total}} = R_1 + R_{23} + R_4 = 36 + 24 + 50 = 110\,\Omega\] \[I = \frac{V_{\text{total}}}{R_{\text{total}}} = \frac{220}{110} = 2 \] \[\text{A}V_{R_4} = I \times R_4 = 2 \times 50 = \boxed{100\,\text{V}}\]Q42: What is the resistance of Light Dependent Resistor (LDR), if the intensity of light is increased?
- Increases
- Decreases
- Remains same
- Becomes infinity
Q43: Which formula is used to calculate the power of a DC circuit?
- Voltage × time
- Current × voltage
- Current × resistance
- Voltage × resistance
Show Explanation
\[ P = V \times I \]Q44: Calculate the hot resistance of 200W / 250V rated lamp.
- 31.25 Ω
- 62.5 Ω
- 312.5 Ω
- 625 Ω
Show Calculation
\[ R = \frac{V^2}{P} = \frac{250^2}{200} = 312.5\,\Omega \]Q45: What is the value of resistance in an open circuit?
- Zero
- Low
- High
- Infinity
Q46: Which resistor the lowest current flows in a parallel circuit having the values of 50 Ω, 220 Ω, 450 Ω and 560 Ω connected with supply?
- 50 Ω
- 220 Ω
- 450 Ω
- 560 Ω
Show Explanation
\[In parallel: I \propto \frac{1}{R} \] \[ → Highest~ resistance = lowest~current \]Q47: What is the specific resistance value of copper conductor?
- 1.72 Ohm/cm³
- 1.72 Micro ohm
- 1.72 Micro ohm.m
- 1.72 Micro ohm.cm
Q48: Which is inversely proportional to the resistance of a conductor?
- Length
- Resistivity
- Temperature
- Area of cross section
Show Explanation
\[ R \propto \frac{l}{A} \Rightarrow R \propto \frac{1}{A} \text{ when length is constant} \] Found a mistake or mismatch in the question or answer? Let us know via email.
This post is licensed under CC BY 4.0 by the author.