Cell and Batteries
Electrician Trade Theory, Module-7
Cell and Batteries
⭕️ Show all Answers
Q1: Which device converts sunlight into electrical energy?
- Photo voltaic cell
- Liquid crystal diode
- Light emitting diode
- Light dependent resistor
Q2: Which law secondary cell works?
- Lenz’s law
- Joule’s law
- Faraday's laws of electrolysis
- Faraday's laws of electromagnetic induction
Q3: How the capacity of batteries is specified?
- Volt
- Watt
- Volt Ampere
- Ampere hour
Q4: What is the name of defect that bending of plates in secondary cells?
- Buckling
- Local action
- Partial short
- Hard sulphation
Q5: What is the unit of electric charge?
- Volt
- Watt
- Ampere
- Coulomb
Q6: What is the output voltage of lithium cell?
- 1.2 V
- 1.5 V
- 1.8 V
- 2.5 V
Q7: What is the method of charging if the battery is to be charged for short duration at higher rate?
- Initial charge
- Boost charge
- Trickle charge
- Freshening charge
Q8: Which electrolyte used in carbon zinc dry cells?
- Dilute sulphuric acid
- Ammonium chloride
- Potassium hydroxide
- Concentrated hydrochloric acid
Q9: Which effect causes by passing electric current in liquids?
- Heating
- Lighting
- Magnetic
- Chemical
Q10: Which material is used to make negative plates in lead acid battery?
- Lead dioxide
- Sponge lead
- Lead peroxide
- Lead sulphate
Q11: Which technique is used to control the corrosion of a metal surface?
- Anodic protection
- Cathodic protection
- Electrolytic protection
- Electrostatic protection
Q12: Which cell is most often used in digital watches?
- Voltaic
- Lithium
- Mercury
- Silver oxide
Q13: What is the effect if one cell is connected with reverse polarity in a parallel combination circuit?
- Voltage become zero
- Become open circuit
- Will get short circuited
- No effect will function normally
Q14: What is the function of fine selector switch in battery charger?
- Selection of current rating
- Selection of charging time
- Selection of voltage range
- Selection of charging method
Q15: What is the effect on output power with respect to temperature in solar cells?
- No effect on change in temperature
- Increases with increase in temperature
- Decreases with increase in temperature
- Decreases with decrease in temperature
Q16: What purpose the hydrometer is used during charging of battery?
- Determine the AH capacity
- Assess the battery voltage level
- Assess the discharge level of battery
- Determine the specific gravity of electrolyte
Q17: What is the formula for Faraday’s first law of electrolysis?
- M = Z/it
- M = Zit
- M = it/Z
- M = Zt/i
Q18: Which is used as an electrolyte in lead acid battery?
- Hydrochloric acid
- Ammonium chloride
- Potassium hydroxide
- Diluted sulphuric acid
Q19: What is the total voltage of the circuit?
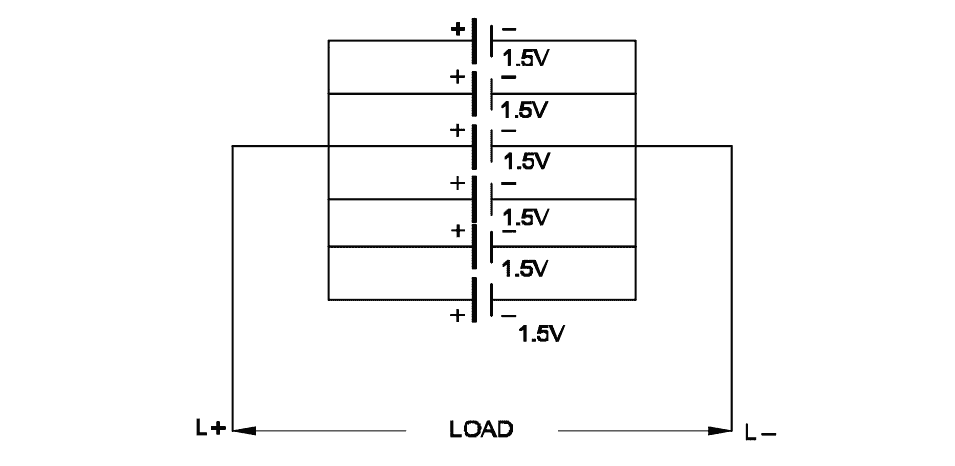
- 1.5 Volt
- 6.0 Volt
- 7.5 Volt
- 9.0 Volt
Show Explanation
In a parallel connection, the voltage remains the same as that of a single cell.
Given: Each cell = 1.5 V, connected in parallel
Total voltage V = 1.5 V
Q20: What is the outcome at the positive plate, after the chemical reaction in lead acid battery during charging?
- Sponge lead (Pb)
- Lead peroxide (PbO₂)
- Lead sulphate (PbSO₄)
- Lead sulphate + water
Q21: Why the vent plug is kept open during charging of a battery?
- To escape the gas freely
- To allow oxygen enter inside
- To check the level of electrolyte
- To check the colour changes in the plates
Q22: In which method the battery is charged at low current for long period?
- Rectifier method
- Trickle charging method
- Constant current method
- Constant potential method
Q23: How the hard sulphation defect in lead acid battery can be rectified?
- Changing with new electrolyte
- Replacing with new electrodes
- Recharging the battery for a longer period at low current
- Recharging the battery for short period at high current
Q24: Which material is used as cathode (-ve) electrode in silver oxide battery?
- Zinc
- Copper
- Carbon
- Silver oxide
Q25: What is the Electro Chemical Equivalent (ECE) of silver?
- 0.001182 mg/coloumb
- 0.01182 mg/coloumb
- 0.1182 mg/coloumb
- 1.1182 mg/coloumb
Q26: What is the outcome of the chemical reaction that takes place in negative plate of lead acid battery during discharging?
- Sponge lead (Pb)
- Lead peroxide (PbO₂)
- Lead sulphate (PbSO₄)
- Lead sulphate + water
Q27: What is the purpose of separator in lead acid battery?
- To provide a path for electrolyte
- To hold the positive and negative plate firmly
- To avoid short in between the positive and negative plates
- To keep positive and negative plate in a sequence array
Q28: Which instrument is used to measure the specific gravity of electrolyte in lead acid battery?
- Barometer
- Hydrometer
- Anima meter
- High rate discharge tester
Q29: Which type of inverter circuit?
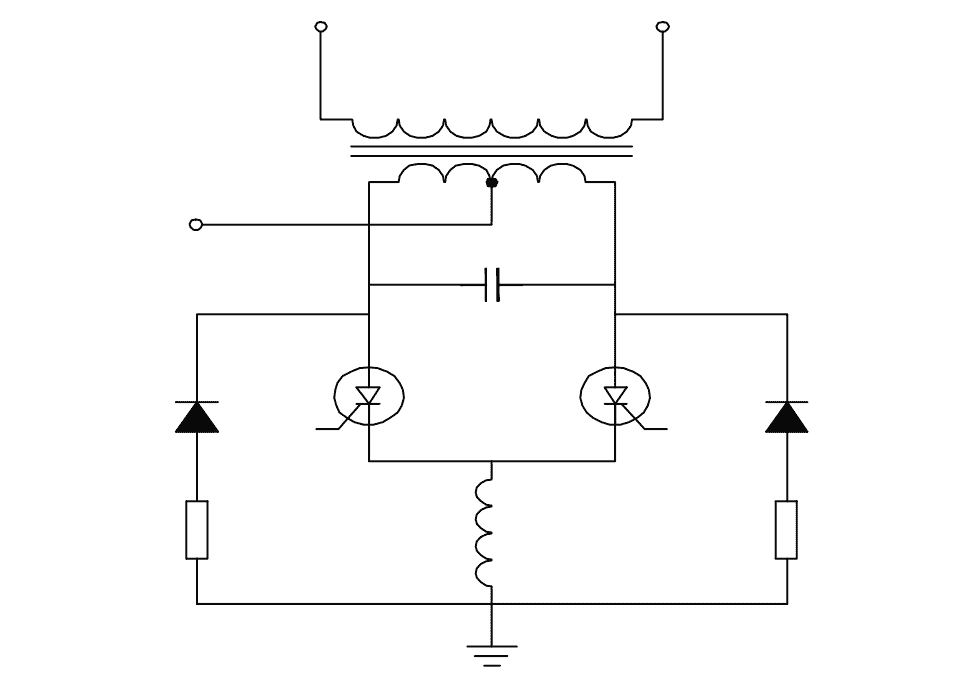
- Driven inverter
- SCR used inverter
- Single transistor inverter
- Two winding transformer inverter
Q30: What is the effect of buckling defect in a lead acid battery?
- Bending of the electrodes
- Reducing the strength of electrolyte
- Making short between the electrodes
- Increasing the internal resistance
Q31: What is the total output voltage of the circuit?
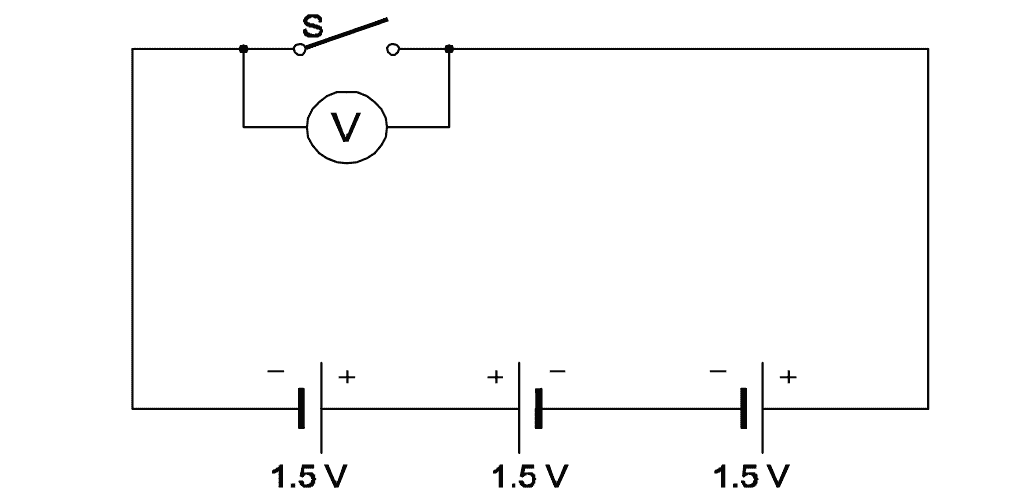
- 0 V
- 1.5 V
- 3.0 V
- 4.5 V
Show Explanation for Q31
Given: 3 cells in series, each of 1.5 V
Total voltage in series is: V = 1.5 V × 3 = 4.5 V
Q32: Which is used as a positive electrode in a dry cell?
- Zinc
- Carbon
- Copper
- Lithium
Q33: What happen to the terminal voltage of a cell if load increases?
- Increases
- Decreases
- Falls to zero
- Remains same
Q34: How local action defect is prevented in voltaic cell?
- By connecting cells in series
- By using a depolarizing agent
- By connecting cells in parallel
- By amalgamating the zinc plate
Q35: What does the letter ‘Z’ indicate in the formula M=Zit?
- Time in seconds
- E.C.E of electrolyte
- Amount of current in Amp
- Mass deposited in grams
Q36: What is the Electro Chemical Equivalent (ECE) of copper?
- 0.329 mg / coulomb
- 0.329 g / coulomb
- 1.1182 mg / coulomb
- 1.1182 g / coulomb
Q37: Which is the cause for buckling defect in lead acid battery?
- Overcharging or over discharging
- Charging with low rate for short period
- Formation of sediments falling from the plate
- Battery is kept in discharged condition for long period
Q38: Which apparatus is used to check the charging condition of voltage in battery?
- Voltmeter
- Multimeter
- Hydrometer
- High rate discharge tester
Q39: Which part is losing electron during electrolysis?
- Cathode
- Anode
- Electrolyte
- Separator
Q40: What is the formula to calculate the Mass deposited during electrolysis?
- M = Z/it gm
- M = Zit gm
- M = it/Z gm
- M = Zt/i gm
Found a mistake or mismatch in the question or answer? Let us know via email.
This post is licensed under CC BY 4.0 by the author.
