Electronic Practice
Electrician Trade Theory, Module-7
Electronic Practice
⭕️ Show all Answers
Q1: Which resistor is used to measure light intensity?
- VDR
- NTC
- PTC
- LDR
Q2: Which code indicates silicon semi conductor diode?
- OA 79
- BY 126
- IN 4007
- 2N 3055
Q3: What is the input ripple frequency (F) of full wave rectifier?
- $F = \frac{1}{2} F_{in}$
- $F = F_{in}$
- $F = 2F_{in}$
- $F = \sqrt{2}F_{in}$
Q4: Which is a active component?
- Inductor
- Resistor
- Capacitor
- Transistor
Q5: Which letter indicates the compound material cadmium sulphide?
- A
- B
- C
- R
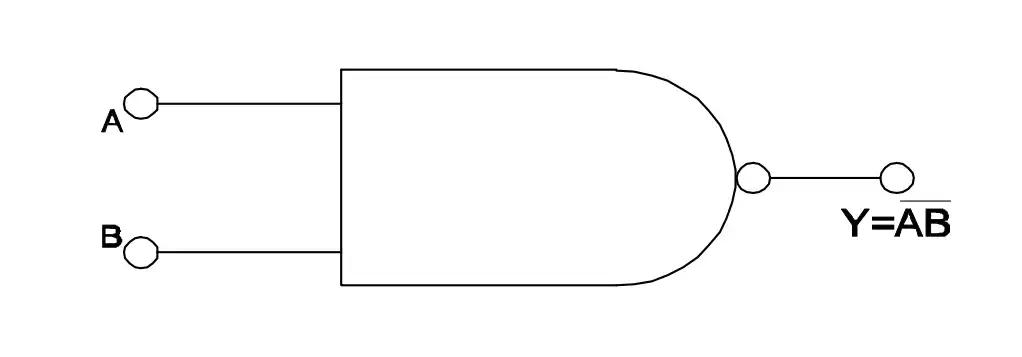
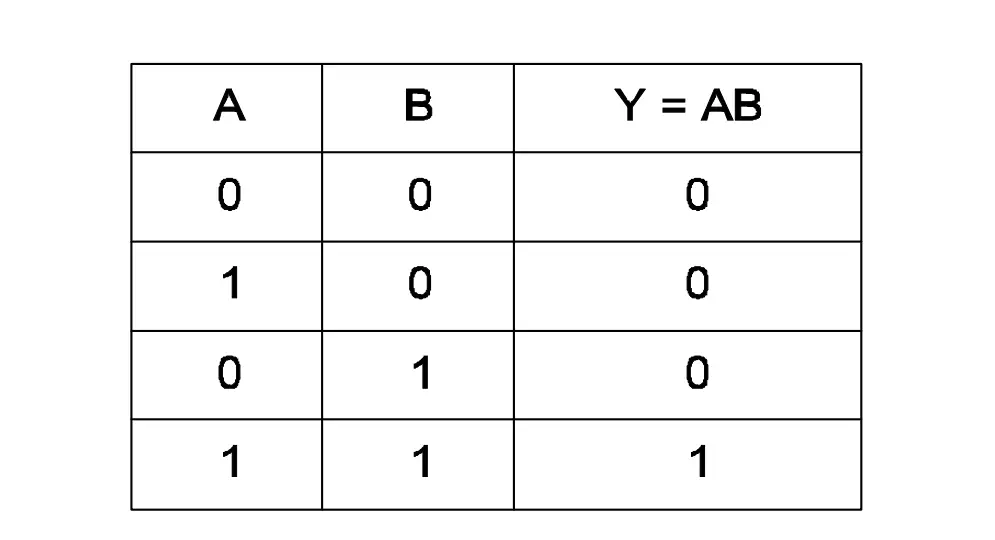
Q6: What is the name of the symbol?
- Two input OR gate
- Two input AND gate
- Two input NOR gate
- Two input NAND gate
Q7: Which is a passive component?
- Diac
- Diode
- Transistor
- Capacitor
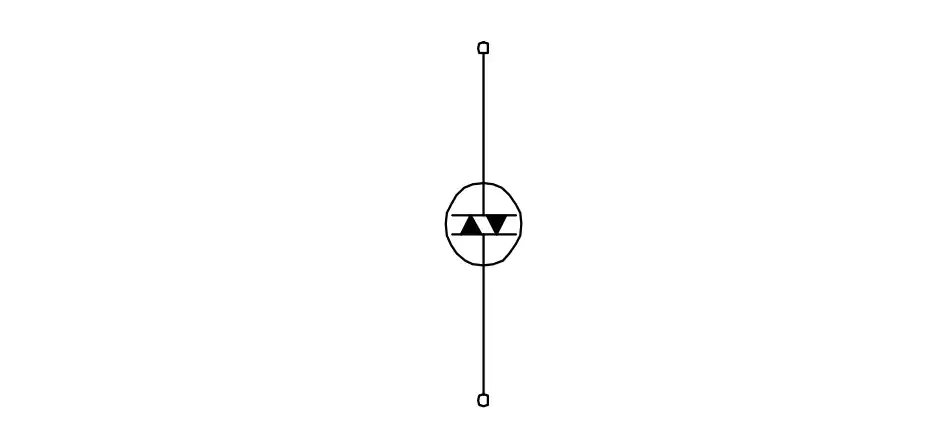
Q8: What is the name of the device symbol?
- SCR
- IGBT
- DIAC
- TRIAC
Q9: How many characters are in hexadecimal number system?
- 6
- 8
- 12
- 16
Q10: Which electronic circuit generates A.C signal without input?
- Filter circuit
- Rectifier circuit
- Amplifier circuit
- Oscillator circuit
Q11: Which instrument provides a visual representation of measured or tested quantities?
- Voltage stabilizer
- Function generator
- Cathode ray oscilloscope
- Radio frequency generator
Q12: What is the name of amplifier?
- Common emitter amplifier
- Class B push pull amplifier
- Common collector amplifier
- Class AB push pull amplifier
Q13: What is the formula to calculate the resonance frequency in an oscillator circuit?
- $F_r = \frac{1}{2LC}$
- $F_r = \frac{1}{\sqrt{2LC}}$
- $F_r = \frac{1}{2\pi\sqrt{LC}}$
- $F_r = \frac{LC}{2\pi}$
Q14: What is the minimum voltage required in the base emitter junction to conduct a silicon transistor?
- 0.2 V - 0.3 V
- 0.4 V - 0.5 V
- 0.6 V - 0.7 V
- 0.8 V - 0.9 V
Q15: What is the minimum and maximum value of resistor with four colour bands, red, violet, orange and gold respectively?
- 237500 - 262500
- 247000 - 273000
- 256500 - 283500
- 224000 - 336000
Show Resistance Calculator
Q16: What is the reason for barrier voltage is more in silicon material?
- Lower atomic number
- Resistance is very low
- Doping percentage is more
- Valance electrons are two only
Q17: What is the reason for widened barrier in a reverse biased diode?
- Minority carriers in two materials are neutralised
- Electron in N material is drifted to positive terminal
- Holes in P material attracted to negative terminal
- Electrons and holes are attracted towards supply terminals
Q18: What is the output voltage in the full wave rectifier circuit?
- No output
- Rated output
- Half the rated output
- Double the rated output
Q19: Which filter circuit is capable of removing voltage spikes in the rectifier circuit?
- LC filter
- RC filter
- Capacitor input filter
- Series inductor filter
Q20: Which is the advanced version of power electronic component used in the output stage in drives?
- FET
- UJT
- SCR
- IGBT
Q21: How the decimal number can be converted into binary number?
- Divide decimal by 4
- Multiplying decimal by 4
- Dividing decimal by 2
- Multiplying decimal 2
Q22: What is the purpose of using binary coded decimal (BCD) system in digital circuits?
- Storing the data inputs
- Control the binary system
- Interface to binary system
- Segregating the input parameters
Q23: Which logic gate refers the truth table?
- OR gate
- NOT gate
- AND gate
- NOR gate
Q24: Which quantity can be measured by CRO?
- Frequency
- Inductance
- Resistance
- Power factor
Q25: Which is the main application of SCR?
- Amplifier
- Oscillators
- Multi vibrators
- Speed control of motors
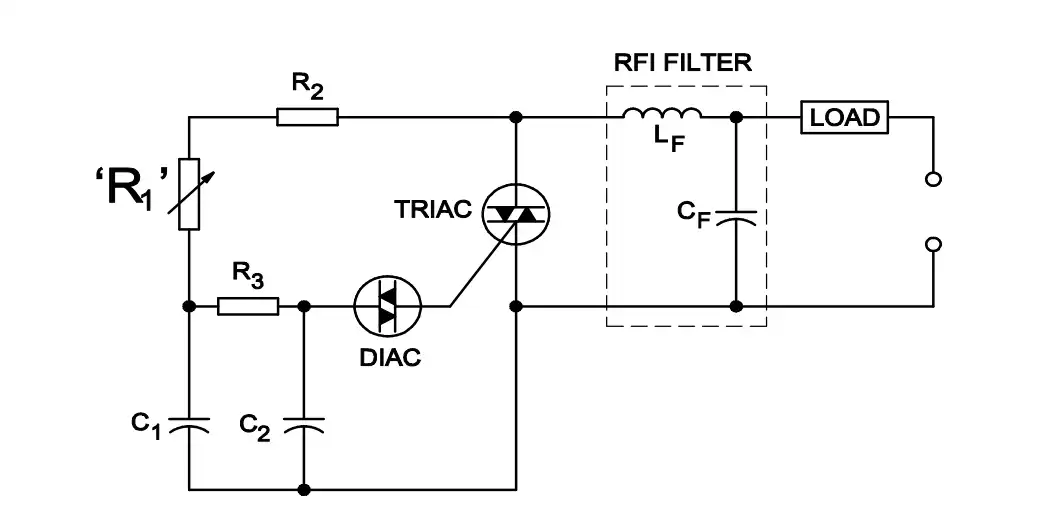
Q26: What is the function of R1 variable resistor?
- Controls the current in R1
- Protects from overload to TRIAC
- Protects the RFI filter from overloading
- Controls the pulse rate for triggering the TRIAC
Q27: What is the purpose of connecting L1 through C1 to the transistor base?
- Provides DC supply
- Provides positive feedback
- Provides negative feedback
- Provides transistor biasing voltage
Q28: What is the criteria to decide a material as conductor, semi conductor and insulator?
- Atomic bonding structure of atom
- Existence of valance electrons in atom
- Atomic weight of the atom of the material
- Atomic number of the atom of the material
Q29: Which doping material is used to make P-type semi conductor?
- Boron
- Arsenic
- Antimony
- Phosphorous
Q30: Which type of biasing is required to a NPN transistor for amplification?
- Base ground, emitter and collector positive
- Base negative, emitter positive and collector negative
- Base positive, emitter negative and collector positive
- Base positive, emitter negative and collector negative
Q31: What is the type of function in the transistor circuit?
- Switching
- Oscillation
- Modulation
- Amplification
Q32: Why negative feedback is required in amplifier circuits?
- To reduce the distortion
- To increase the amplification factor
- To increase the output voltage gain
- To increase the output current gain
Q33: What is the purpose of DIAC in power control circuits?
- As rectifier
- For triggering
- As an oscillator
- For amplification
Q34: Which type of control device is used in electronic fan regulator control circuits?
- FET
- UJT
- DIAC
- TRIAC
Q35: Which quadrant operation of SCR delivers heavy current in reverse biasing?
- First quadrant
- Third quadrant
- Fourth quadrant
- Second quadrant
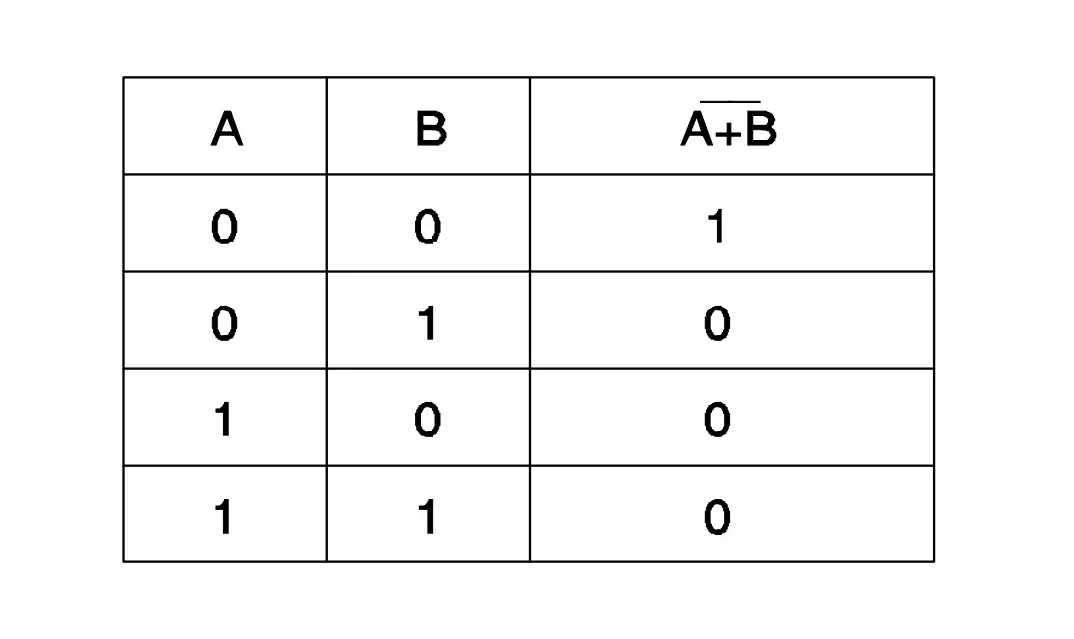
Q36: Which logic gate refers the truth table?
- AND
- NOT
- NOR
- NAND
Q37: What is the use of timebase control switch or knob in the CRO?
- Select sweep speed
- Select input voltage range
- Select input signal voltage
- Select intensity of the beam
Q38: Why a snubber circuit is used in the TRIAC motor control circuit?
- To avoid false triggering
- To increase the life of TRIAC
- To increase the motor torque
- To maintain the motor speed constant
Q39: What is the output DC voltage in half wave rectifier, if the input AC voltage is 24 volt?
- 24 Volt
- 12 Volt
- 9.6 Volt
- 10.8 Volt
Show Calculation
$V_{dc} = \frac{V_{max}}{\pi}$ Input AC Voltage ($V_{rms}$) = $24 \text{ V}$ $V_{max} = V_{rms} \times \sqrt{2}$ $V_{max} = 24 \times 1.414$ $V_{max} = 33.936 \text{ V}$ $V_{dc} = \frac{33.936}{\pi}$ $V_{dc} = \frac{33.936}{3.1416}$ $V_{dc} \approx 10.8 \text{ V}$ **Short Method:** $$V_{dc} = 0.45 \times 24 = 10.8 \text{ V}$$Q40: Why most of semi conductor devices are made by silicon compared to germanium?
- High barrier voltage
- High resistance range
- High thermal conductivity
- High current carrying capacity
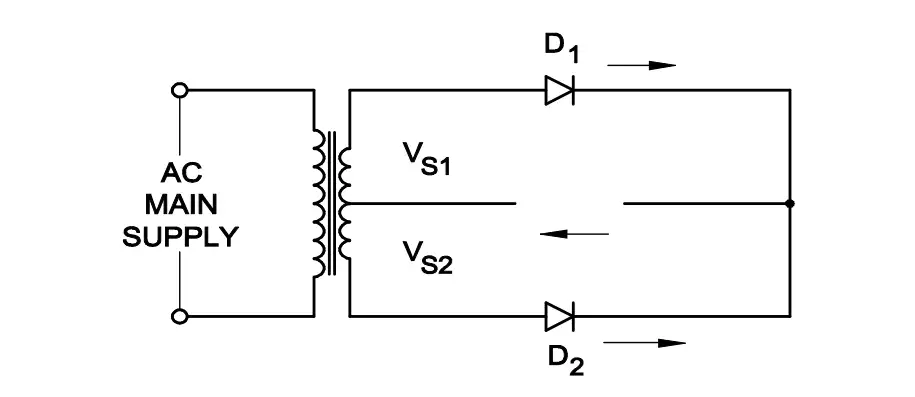
Q41: What is the output voltage if the centre tap of transformer is open circuited in a full wave rectifier circuit?
- Zero voltage
- Full rated output
- Half of the rated output
- One fourth of rated output
Q42: Which oscillator provides high accurate stable frequency?
- Hartley oscillator
- Colpitts oscillator
- Quartz crystal oscillator
- R.C phase shift oscillator
Q43: What is the characteristic property of base material in a transistor?
- Lightly doped and very thin
- Heavily doped and very thin
- Lightly doped and very larger
- Heavily doped and very larger
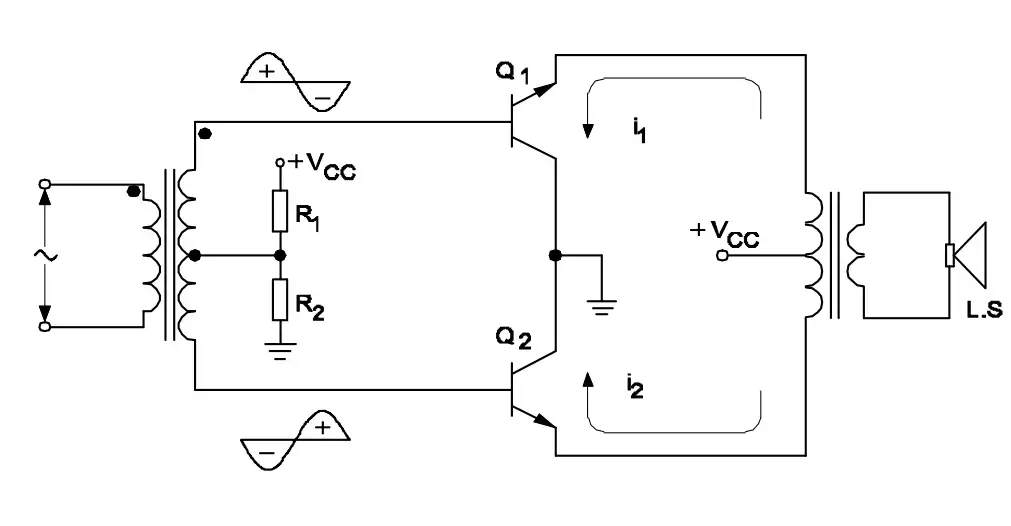
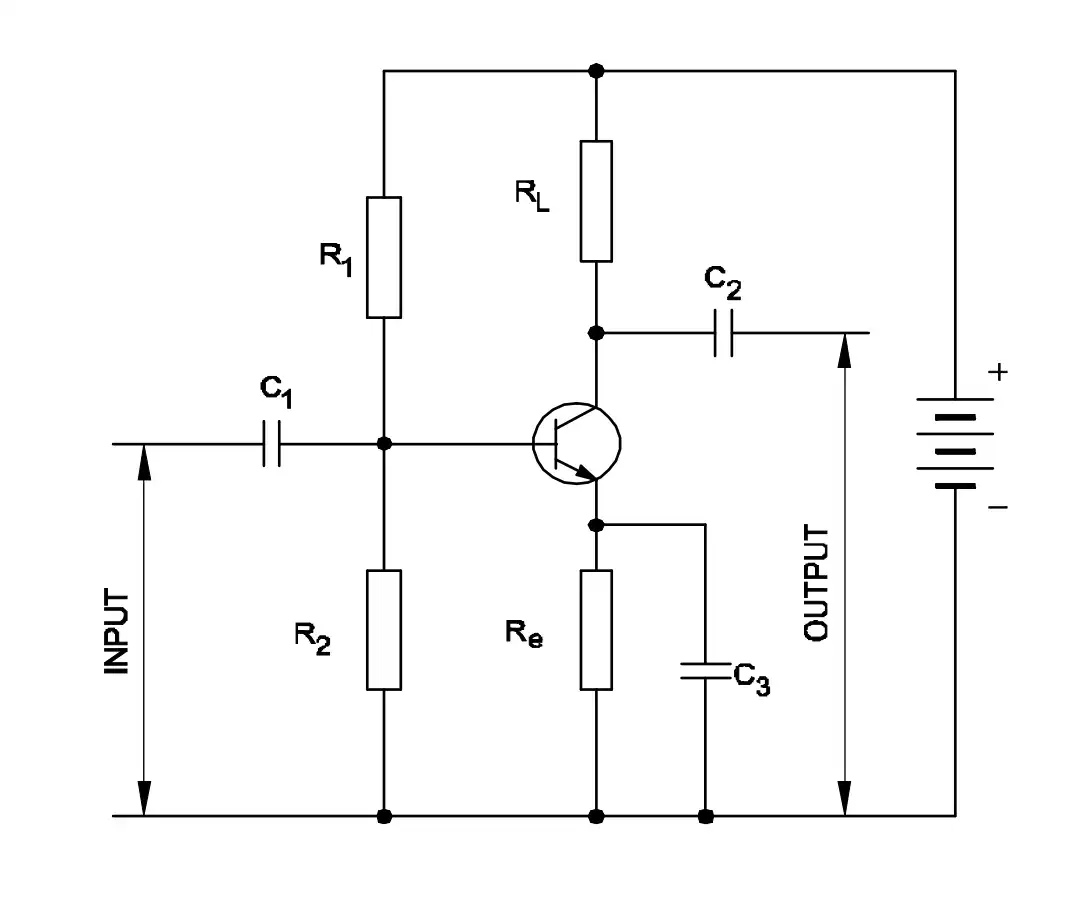
Q44: What is the type of amplifier?
- Push Pull Amplifier
- Common Base Amplifier
- Emitter Follower Amplifier
- Common Emitter Amplifier
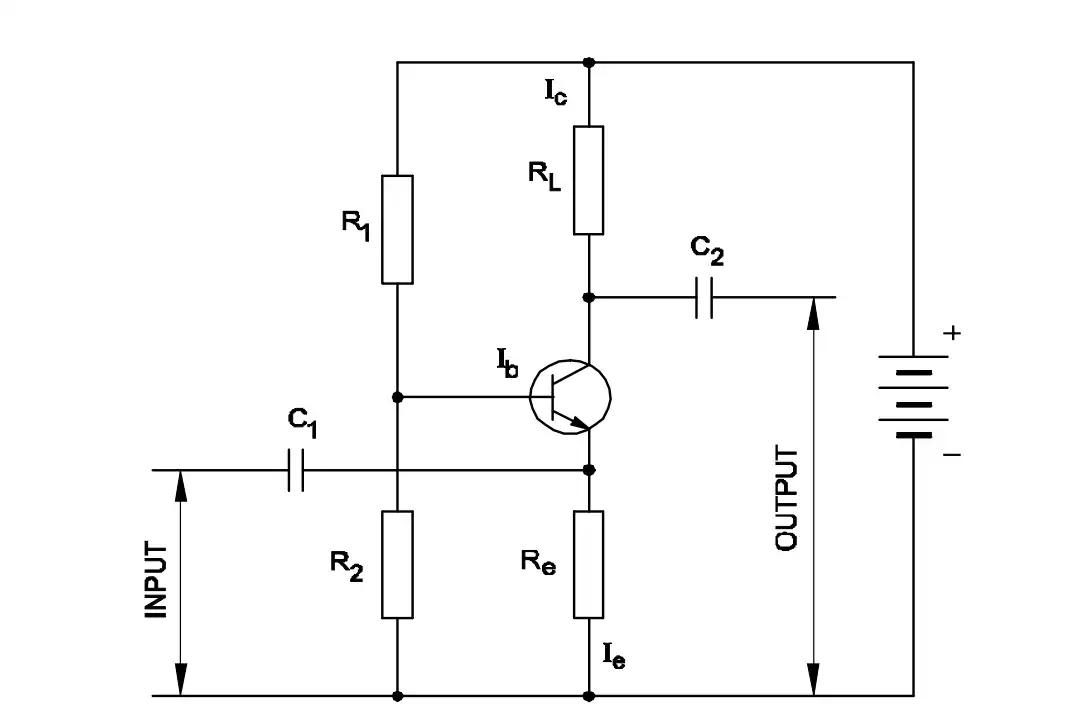
Q45: Which resistor determines the voltage gain in a common emitter amplifier?
- $R_1$
- $R_2$
- $R_L$
- $R_e$
Q46: Which multi vibrator produces a repetitive pulse wave form output?
- Astable multi vibrator
- Bistable multi vibrator
- One shot multi vibrator
- Monostable multi vibrator
Q47: Why a feedback network is used in the oscillator?
- To cancel noise distortion
- To phase shift the signal by 60°
- To phase shift the signal by 180°
- To cancel second harmonic distortion
Q48: What is the main application of a Field Effect Transistor (FET)?
- Voltage control device
- Current control device
- Positive feedback device
- Low input impedance device
Q49: What is the main function of Uni Junction Transistor (UJT)?
- Relaxation oscillator
- Broadcast transmitter
- Loud speaker amplifier
- Microphone input device
Q50: How the gate terminal of N channel JFET biased?
- Gates are reverse biased
- Gates are forward biased
- Gates are forward biased with drain
- Gates are reverse biased with source
Q51: What is the total turn-on time ($t_{on}$) while transistor makes a transition from $V_2$ to $V_1$?
- $t_{on} = t_r - t_d$
- $t_{on} = t_r \times t_d$
- $t_{on} = t_d + t_r$
- $t_{on} = t_d / t_r$
Q52: Which device is made up of using the methods of point contact, grown, diffusion and alloy junctions?
- Inductor
- Resistor
- Capacitor
- Transistor
Q53: Why the collector region is physically made larger than emitter region in a transistor?
- It has to dissipate more heat
- Output taken from collector terminal
- Base collector region is reverse biased
- Collector region always operate with high voltage
Q54: What is the function of a transistor if emitter to base and collector to base are forward biased?
- Acts as an amplifier
- Acts as an oscillator
- Acts as an open circuit
- Acts as a closed switch
Q55: What is the main advantage of a class A amplifier?
- Minimum distortion
- Maximum current gain
- Maximum voltage gain
- Minimum signal to noise ratio losses
Q56: Which electronic circuit produces signal waves or pulses without an input?
- Detector
- Amplifier
- Oscillator
- Modulator
Q57: Which circuit is essential to maintain oscillations or waves in an oscillator circuit?
- Rectifier with filter
- Voltage multiplier
- Negative feed back
- Positive feed back
Q58: What is the main application of uni junction transistor?
- Rectification
- Amplification
- Regulator circuits
- Triggering circuits
Q59: Which device has very high input impedance, low noise output, good linearity and low inter electrode capacity?
- NPN transistor
- PNP transistor
- Field effect transistor
- Uni junction transistor
Q60: What is the difference in current control of MOSFET compared to JFETs?
- Insulating layer instead of junction
- Using N material instead of P material
- Using P material instead of N material
- Using N material gate instead of P material
Q61: What is the type of amplifier circuit?
- Common base amplifier
- Common emitter amplifier
- Class B push pull amplifier
- Common collector amplifier
Q62: What is the peak voltage of 220V rms AC voltage?
- 310.02 V
- 311.17 V
- 312.25 V
- 315.20 V
Q63: How the input impedance of CRO can be increased?
- By adding resistance to CRO probe
- By adding resistance to trigger level circuit
- By increasing time/base attenuator switch position
- By increasing volts/cm attenuator switch position
Q64: What is the frequency of the displayed signal on CRO screen covered by 5 division with a time base setting of 0.2 micro seconds?
- 1.0 KHz
- 10.0 KHz
- 100.0 KHz
- 1000.0 KHz
Show Calculation
$T = \text{Number of divisions} \times \text{Time base setting}$ $F = \frac{1}{T}$ * Number of divisions = $5$ * Time base setting = $0.2 \text{ } \mu\text{s/div}$ (microseconds) $T = 5 \times 0.2 \text{ } \mu\text{s}$ $T = 1.0 \text{ } \mu\text{s}$ $T = 1.0 \times 10^{-6} \text{ seconds}$ $F = \frac{1}{1.0 \times 10^{-6}}$ $F = 1,000,000 \text{ Hz}$ $F = 1000 \text{ kHz}$Q65: What defect will occur in the radio, if the pulsations are not removed from the input of the rectifier?
- Improper tuning
- No response
- Humming sound
- Works with low volume
Q66: How does the depletion region behave?
- As resistor
- As insulator
- As conductor
- As semi conductor
Q67: What is the power gain of CE amplifier with a voltage gain of 66 and $\beta$ (Beta) of the transistor is 100?
- 1.5
- 166
- 0.66
- 6600
Show Calculation
The Power Gain ($A_p$) of a Common Emitter (CE) amplifier is the product of its Voltage Gain ($A_v$) and Current Gain ($A_i$). For a CE configuration, the current gain is approximately equal to the transistor's Beta ($\beta$). $A_p = A_v \times A_i$ $A_p \approx A_v \times \beta$ * Voltage Gain ($A_v$) = $66$ * Transistor Beta ($\beta$) = $100$ $A_p = 66 \times 100$ $A_p = 6600$Q68: What is the effect, if SCR is latched into conduction and gate current is removed in DC?
- SCR gets cut off
- Current through SCR OFF
- Output voltage will be reduced
- Gate looses control over conduction
Q69: What is the effect of pinch-off voltage in JFET?
- No depletion region exists
- Drain current becomes zero
- Reverse bias voltage becomes zero
- Width of channel has maximum value
Found a mistake or mismatch in the question or answer? Let us know via email.
This post is licensed under CC BY 4.0 by the author.