Transmission and Distribution
Electrician Trade Theory, Module-12
Transmission and Distribution
⭕️ Show all Answers
Q1: Which electric lines connect the substation to distributors in distribution system?
- Feeders
- Distributors
- Service lines
- Service mains
Q2: What is the insulation resistance between any two conductors in a medium voltage domestic installation as per IE rules?
- Infinity
- More than one Mega ohm
- More than two Mega ohms
- More than three Mega ohms
Q3: What is the voltage ratio in A.C distribution line adopted for domestic consumers?
- 415 V/240 V
- 240 V/110 V
- 415 V/110V
- 11 KV/415 V
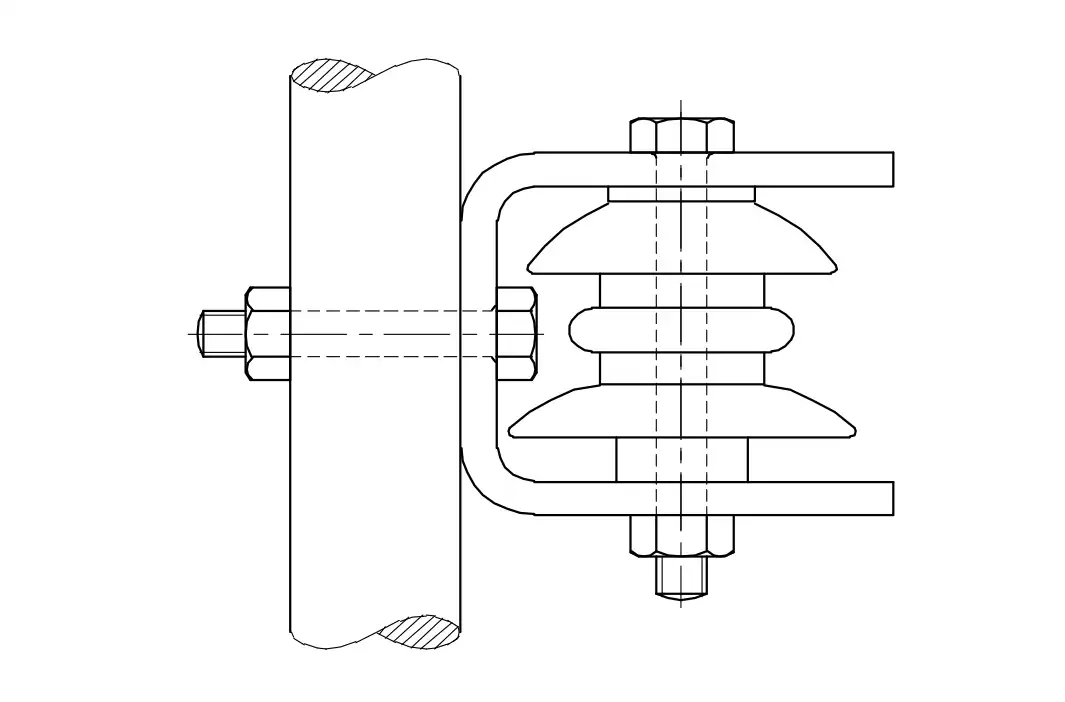
Q4: What is the name of the insulator used in O.H lines?
- Pin insulator
- Post insulator
- Strain insulator
- Shackle insulator
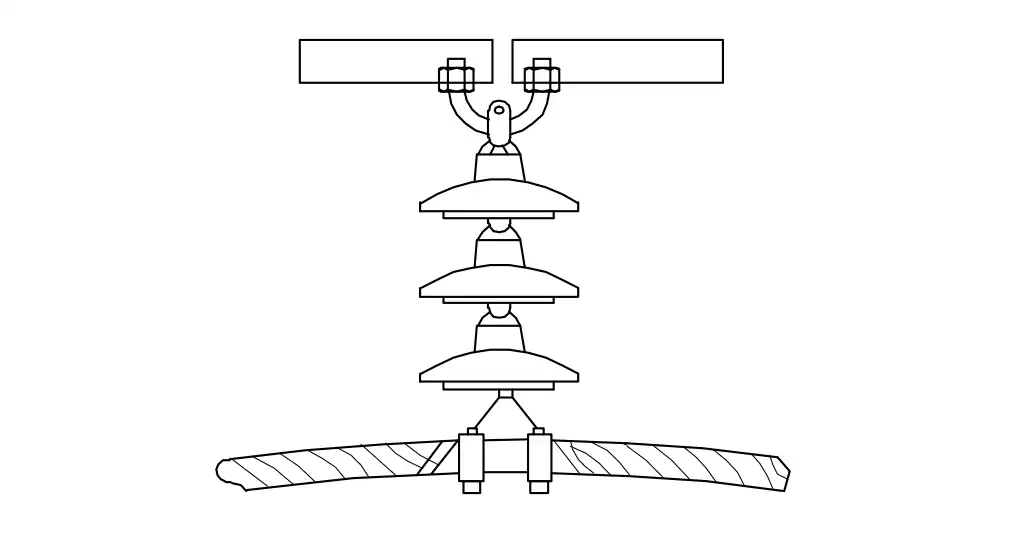
Q5: What is the name of line insulator?
- Pin type insulator
- Disc type insulator
- Shackle type insulator
- Suspension type insulator
Q6: Which is the permissible load for lighting subcircuit in domestic wiring as per IE rules?
- 800 W
- 1200 W
- 2400 W
- 3000 W
Q7: What is the name of the insulator?
- Stay insulator
- Shackle insulator
- Suspension insulator
- Single shed pin insulator
Q8: What is the reason for the conductor cross-sectional area can fully utilised on transmission of DC as compared to AC?
- No heat loss
- No skin effect
- No power loss
- No corona loss
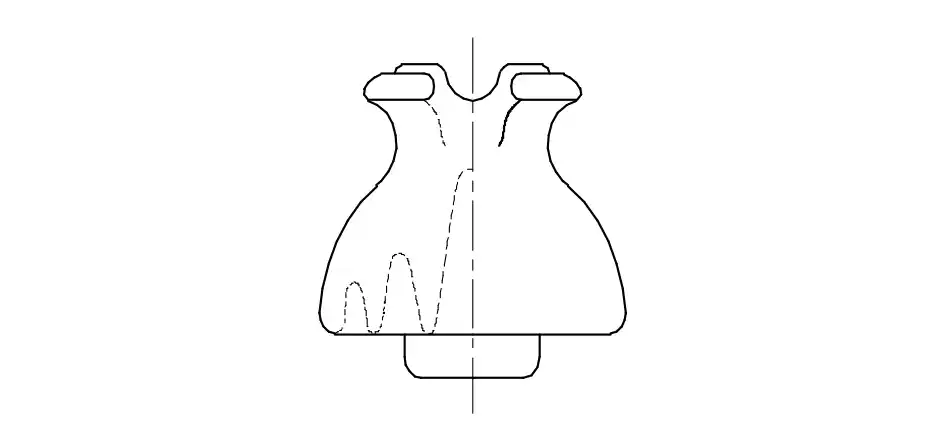
Q9: Why the disc pin insulators outer surface is made by glazing and bent the sides inward?
- To withstand high voltage
- Not to attract birds to sit on it
- To offer high mechanical strength
- Disables continuous water flow in rainy season
Q10: What is the type of over head line joint?
- Twisted joint
- Straight sleeve joint
- Compression joint for ACSR
- Straight joint through connectors
Q11: Why steel is reinforced in ACSR conductors used for over head lines?
- To minimize the line sag
- To reduce the line voltage drop
- To increase the tensile strength
- To increase the current carrying capacity
Q12: Which type of A.C transmission is universally adopted?
- Two phase four wire
- Two phase three wire
- Single phase two wire
- Three phase three wire
Q13: Which type of line insulator is used for terminating on corner post?
- Pin insulator
- Strain insulator
- Shackle insulator
- Suspension insulator
Q14: What is the reason of keeping binding wire gap too close and very tight in pin insulator?
- Avoid sparking
- Avoid corrosion
- Avoid oxide formation
- Avoid atmospheric pressure
Q15: What is the name of conductor used on overhead lines?
- ACSR
- Aluminium
- Galvanised iron
- Hard drawn copper
Q16: What is the main purpose of crossarm used in electric poles?
- Supporting the line conductors
- Holding the insulators on overhead line
- Avoids short circuit between conductors
- Reduces conductor sag between supports
Q17: Which type of line insulator is used at the dead ends of the H.T overhead lines?
- Pin insulator
- Disc insulator
- Stay insulator
- Post insulator
Q18: What is the advantage of AC power transmission?
- Corona loss negligible
- Stress on transmission lines is minimum
- Low voltage drop in transmission lines
- Voltages can be stepped up and stepped down easily
Q19: What is ACSR stands for?
- All Conductors Steel Reinforced
- Aluminium Core Steel Reinforced
- Aluminium Covered Steel Reinforced
- Aluminium Conductor Steel Reinforced
Q20: What is the purpose of cross-arm in O.H lines?
- Provide more support to the O.H pole
- Protect from short between conductors
- Reduce the sag of the lines between poles
- Holding the insulators where the conductors are fastened
Q21: What is the advantage of over head lines compared to underground cable?
- Public safety is more
- Faults can be located easily
- No interference with the communication lines
- Not liable to the hazards from lightning discharges
Q22: Which substation the transmission line voltage is stepped down to consumer supply voltage?
- Mobile substation
- Mining substation
- Secondary substation
- Distribution substation
Q23: What will happen to the string arrangement of disc insulators, if one of the disc insulator gets damaged?
- Whole string become useless
- No effect operates normally
- Only the damaged disc will not function
- Damaged insulator and the adjacent insulator will not function
Q24: How the sparking on the aluminium cored conductors binding joints can be prevented?
- Keeping binding turns very close
- Making binding turns very tight
- Providing guard wires below the conductors
- Providing more than one binding
Q25: What will happen to the skin effect on the O.H conductors, if the conductor diameter is small (<1cm)?
- Becomes negligible
- Increases to maximum
- No effect, remain same
- Decreases half of the value
Found a mistake or mismatch in the question or answer? Let us know via email.
This post is licensed under CC BY 4.0 by the author.