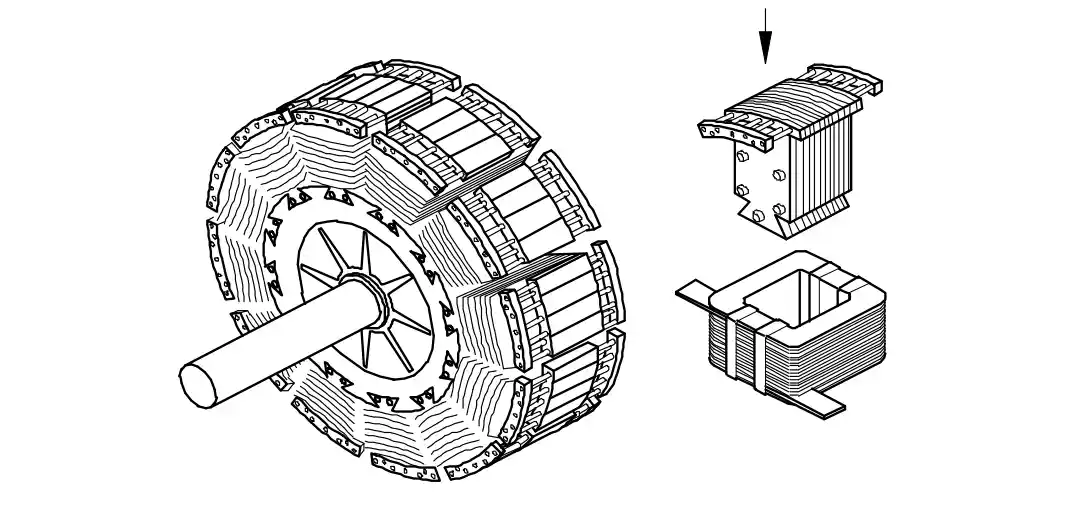
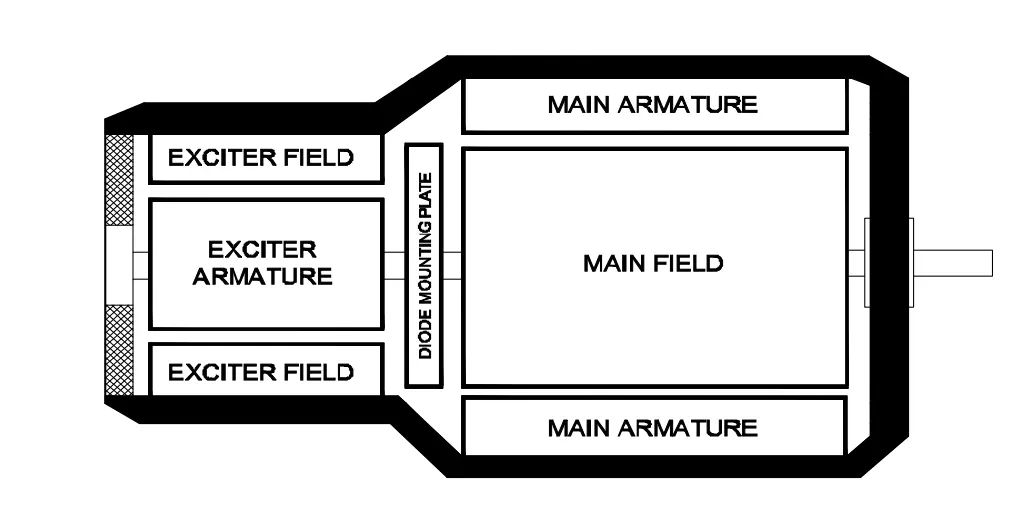
Alternator
Electrician Trade Theory, Module-5
Alternator
⭕️ Show all Answers
Q1: Which formula is used to calculate EMF/phase in a ideal alternator?
- $E = \frac{\phi F T}{2.22}$
- $E = \frac{\phi F T}{4.44}$
- $E = 2.22 \phi F T$
- $E = 4.44 \phi F T$
Q2: Which rule is used to find the direction of induced emf in an alternator?
- Cork screw rule
- Right hand palm rule
- Fleming's left hand rule
- Fleming's right hand rule
Q3: What is the name of the part of alternator?
- Stator
- Exciter
- Salient pole rotor
- Smooth cylindrical rotor
Q4: What is the formula to calculate emf equation of an alternator?
- $E = 4.44 K_d K_c T \phi$
- $E = 2.22 K_d K_c F \phi$
- $E = 4.44 K_d K_c F T \phi$
- $E = 1.11 K_d K_c F \phi$
Q5: How alternators are rated?
- KVA
- KW
- MW
- KV
Q6: Which formula is used to calculate the percentage voltage regulation in alternator?
- $\frac{V_{NL} - V_{FL}}{V_{NL}} \times 100$
- $\frac{V_{NL} - V_{FL}}{V_{FL}} \times 100$
- $\frac{V_{NL} - V_{FL}}{V_{NL}} \times 100$
- $\frac{V_{FL} - V_{NL}}{V_{FL}} \times 100$
Q7: What is the supply frequency of an alternator having 6 poles runs at 1000 rpm?
- 25 Hz
- 40 Hz
- 50 Hz
- 60 Hz
Q8: Calculate the speed of an alternator having 2 poles at a frequency of 50 Hz.
- 1500 rpm
- 2500 rpm
- 3000 rpm
- 6000 rpm
Show Calculation
**Formula:** $N_s = \frac{120 \times f}{P}$ Where: $N_s$ = Synchronous speed in Revolutions Per Minute (RPM) $f$ = Frequency in Hertz (Hz) = 50 Hz $P$ = Number of poles = 2 $N_s = \frac{120 \times 50}{2}$ $N_s = \frac{6000}{2}$ $N_s = 3000$Q9: What condition the lamps become dark in dark lamp method of parallel operation of two alternators?
- Terminal voltages are equal
- Voltage and frequency are equal
- Voltage and power rating are equal
- Frequency are same in both alternator
Q10: How to compensate de-magnetizing effect due to armature reaction in an alternator?
- Reducing the speed of alternator
- Reducing field excitation current
- Increasing field excitation current
- Increasing the speed of alternator
Q11: What is the use of synchroscope?
- Adjust the output voltage
- Adjust the phase sequence
- Adjust the supply frequency
- Indicate the correct instant for paralleling
Q12: What is the name of the equipment that provides D.C to the rotor of alternator?
- Exciter
- Inverter
- Converter
- Synchroniser
Q13: What is the purpose of damper winding in alternator?
- Reduces the copper loss
- Reduces windage losses
- Reduces the hunting effect
- Improves the voltage regulation
Q14: Which condition is to be satisfied before parallel operation of alternators?
- Rating must be same
- Phase sequence must be same
- Rotor impedance must be same
- Stator impedance must be same
Q15: What is the speed of an alternator connected with a supply frequency of 50 Hz at rated voltage having 4 poles?
- 1000 rpm
- 1500 rpm
- 3000 rpm
- 4500 rpm
Show Calculation
**Formula:** $N_s = \frac{120 \times f}{P}$ Where: $N_s$ = Synchronous speed in Revolutions Per Minute (RPM) $f$ = Frequency in Hertz (Hz) = 50 Hz $P$ = Number of poles = 4 $N_s = \frac{120 \times 50}{4}$ $N_s = \frac{6000}{4}$ $N_s = 1500$Q16: What condition the two lamps become bright and one lamp dark during paralleling of two alternators?
- Terminal voltages are equal
- Voltages and frequencies are equal
- Voltages and phase sequence are equal
- Both the alternators receive same frequency
Q17: What causes the terminal voltage of an alternator reduces, if the load increases?
- Field resistance
- Armature reaction
- Inductive reactance
- Armature resistance
Q18: What is the purpose of using damper winding in AC generator?
- Prevents heating
- Reduces copper loss
- Reduces windage loss
- Prevents the hunting effect
Q19: What is the type of alternator?
- Brushless alternator
- Three phase alternator
- Single phase alternator
- Salient pole type alternator
Q20: Calculate the speed in r.p.s of the 2 pole, 50Hz alternator?
- 50 rps
- 100 rps
- 1500 rps
- 3000 rps
Show Calculation
Number of poles ($P$) = $2$ Frequency ($f$) = $50 \text{ Hz}$ **Formula:** $\text{Speed (r.p.s)} = \frac{2 \times f}{P}$ $\text{Speed (r.p.s)} = \frac{2 \times 50}{2} = \frac{100}{2} = 50 \text{ r.p.s}$Q21: What is the advantage of using rotating field type alternator?
- Easy to locate the faults in the field
- Easy to connect the load with alternator
- Easy to dissipate the heat during running
- Two slip rings only required irrespective of No. of phases
Q22: What is the effect in increasing the field excitation current in alternator?
- Prevents demagnetizing
- Over voltage protection
- Dead short circuit protection
- Alternator will be over loaded
Q23: Calculate the pitch factor ($K_p$) for a winding having 36 stator slots 4 pole with angle ($\alpha$) is 30° in alternator.
- 0.942
- 0.965
- 0.978
- 0.985
Show Calculation
$K_p = \cos\left(\frac{\alpha}{2}\right)$ Where: * $\alpha$ = Short pitch angle in electrical degrees (given as $30^\circ$) $K_p = \cos\left(\frac{30^\circ}{2}\right)$ $K_p = \cos(15^\circ)$ $K_p = 0.9659$Q24: What is the cause for hunting effect in alternators?
- Due to over load
- Running without load
- Running with fluctuation of speed
- Due to continuous fluctuation in load
Q25: Calculate the voltage regulation in percentage if the load is removed from an alternator, the voltage rises from 480V to 660V
- 27.2%
- 32.5%
- 37.5%
- 38.5%
Show Calculation
$\%VR = \frac{V_{NL} - V_{FL}}{V_{FL}} \times 100$ $\%VR = \frac{660 - 480}{480} \times 100$ $\%VR = \frac{180}{480} \times 100$ $\%VR = 0.375 \times 100$ $\%VR = 37.5\%$ Found a mistake or mismatch in the question or answer? Let us know via email.
This post is licensed under CC BY 4.0 by the author.