DC Generator
Electrician Trade Theory, Module-1
DC Generator
⭕️ Show all Answers
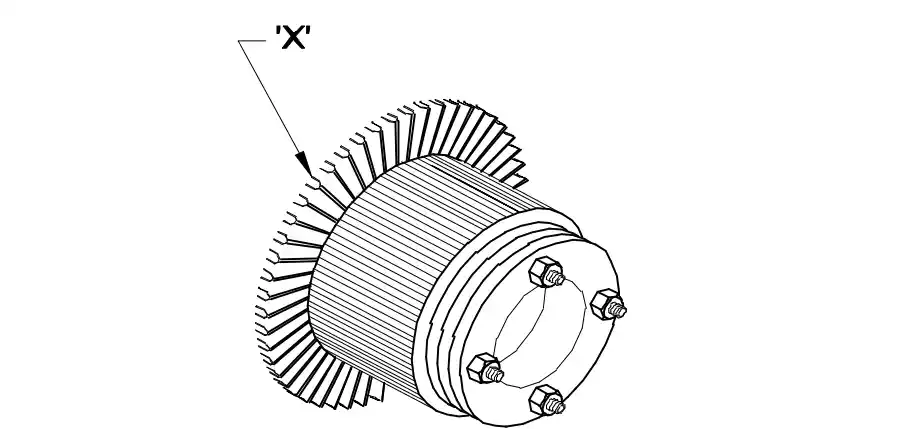
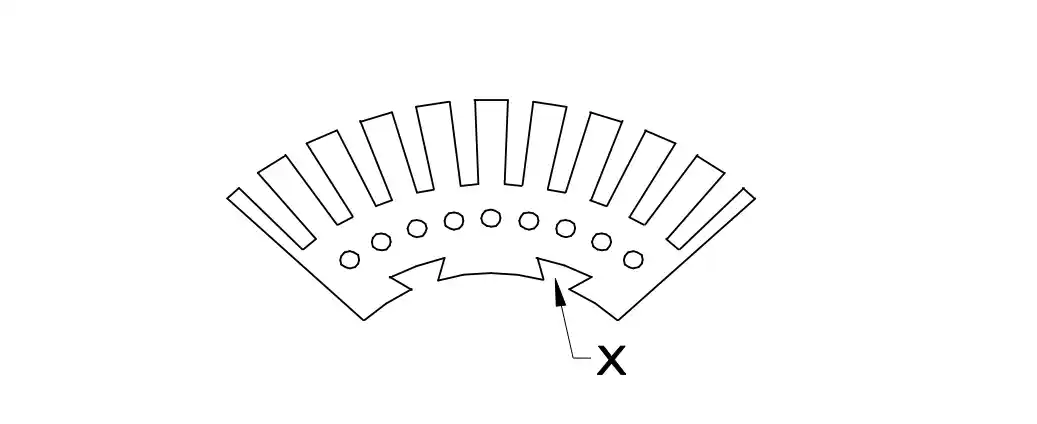
Q1: What is the name of the part marked as 'X' in DC generator?
- Armature core
- Brush
- Commutator raiser
- Commutator segment
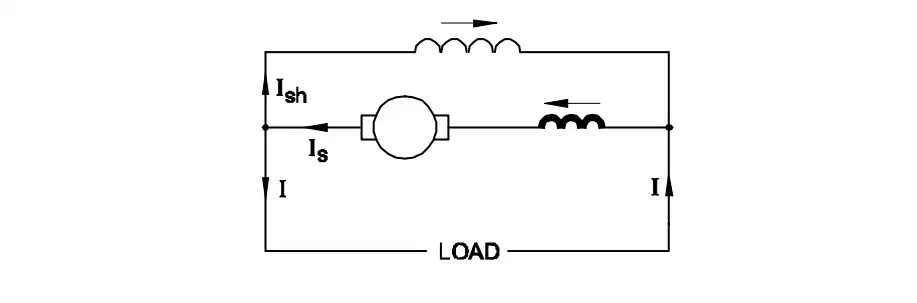
Q2: What is the name of D.C generator?
- Differential long shunt compound
- Differential short shunt compound
- Cumulative long shunt compound
- Cumulative short shunt compound
Q3: Which rule is used to find the direction of induced emf in D.C generator?
- Cork screw rule
- Right hand palm rule
- Fleming's left hand rule
- Fleming's right hand rule
Q4: Which formula is used to calculate the generated emf in D.C generator?
- $\frac{\phi ZN}{60}$ volts
- $\frac{\phi ZNP}{60}$ volts
- $\frac{\phi ZNP}{60A}$ volts
- $\frac{\phi ZNPA}{60}$ volts
Q5: What is the formula to calculate back emf of a D.C motor?
- $E_b = \frac{V}{I_aR_a}$ Volts
- $E_b = V \times I_aR_a$ Volts
- $E_b = V - I_aR_a$ Volts
- $E_b = V + I_aR_a$ Volts
Q6: What is the name of the part marked 'X' in DC generator?
- Pole tip
- Pole coil
- Pole core
- Pole shoe
Q7: What is the name of the D.C generator?
- Shunt generator
- Series generator
- Compound generator
- Separately excited generator
Q8: Which energy is converted into electrical energy by generator?
- Heat
- Kinetic
- Chemical
- Mechanical
Q9: What is the name of D.C generator's field?
- Short shunt compound generator
- Long shunt compound generator
- Differential compound generator
- Cumulative compound generator
Q10: What is the principle of D.C generator?
- Cork screw rule
- Fleming's left hand rule
- Fleming's right hand rule
- Faraday's laws of electromagnetic induction
Q11: What is the formula for dynamically induced emf?
- BLV volts
- BL sin$\theta$ volts
- BLV sin$\theta$ volts
- BLV cos$\theta$ volts
Q12: Which rule is used to find direction of magnetic field?
- Cork screw rule
- Right hand palm rule
- Fleming's left hand rule
- Fleming's right hand rule
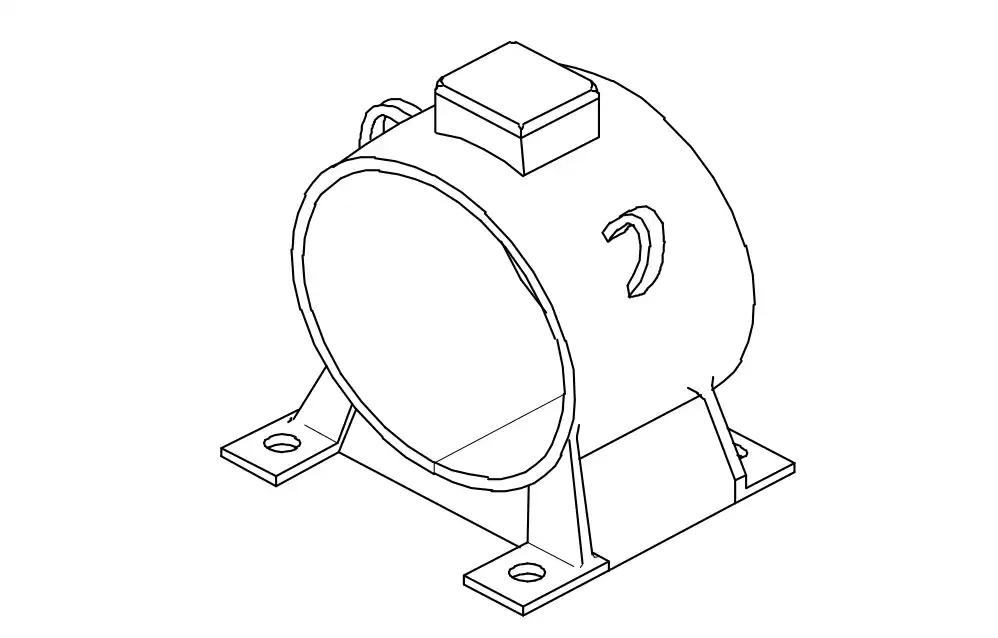
Q13: What is the name of the part of DC generator?
- Stator
- Pole core
- Pole shoes
- Yoke (or) frame
Q14: How many parallel paths in duplex lap winding of a 4 pole DC generator?
- 4
- 6
- 8
- 12
Q15: Name the part of DC generator?
- Side end plates
- Pole shoe lamination
- Commutator segment
- Armature core lamination
Q16: How interpoles are connected in a DC generator?
- In series with armature
- In parallel with armature
- In series with shunt field
- In parallel with shunt field
Q17: What is the necessity of residual magnetism in a self excited DC generator?
- Build up the voltage
- Reduce the field current
- Reduce armature current
- Maintain constant output voltage
Q18: Which are the two points that the brush contact resistance measured in D.C machines?
- Resistance between the opposite brushes
- Resistance between brush and commutator raiser
- Resistance between brush and commutator
- Resistance between brush and armature conductors
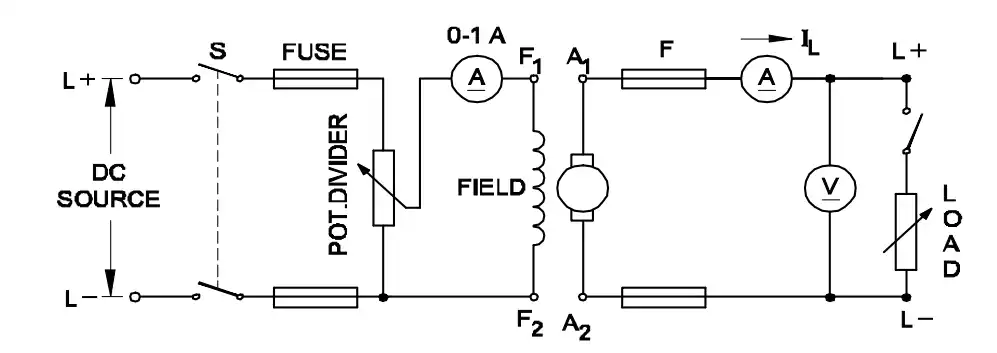
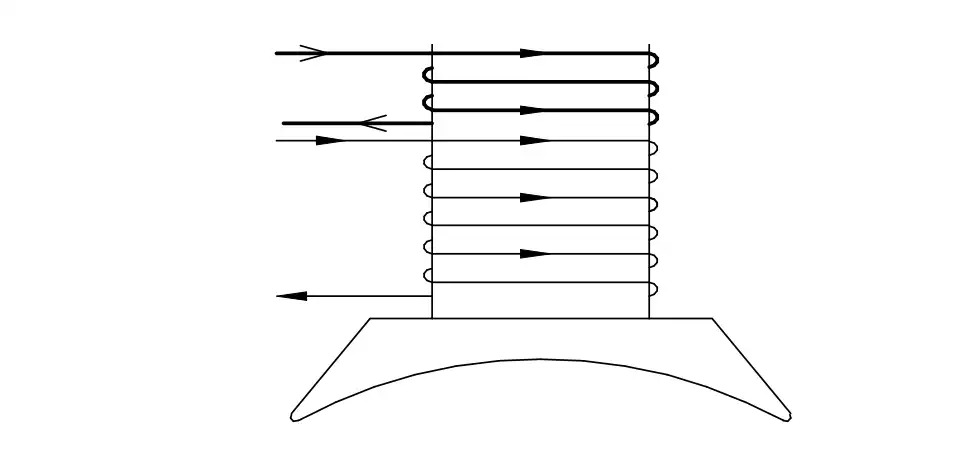
Q19: Which voltage drop is indicated in the portion marked as 'X'?
- Full load voltage drop
- Armature voltage drop
- Armature reaction drop
- Shunt field voltage drop
Q20: What is the name of the compound generator, if the shunt field is connected in parallel with armature?
- Cumulative compound
- Long shunt compound
- Differential compound
- Short shunt compound
Q21: Why the armature core of a DC generator is laminated?
- Reduce the copper loss
- Reduce the friction loss
- Reduce the hysteresis loss
- Reduce the eddy current loss
Q22: Why armature resistance of a D.C generator is very low?
- Reduce armature current
- Reduce armature voltage drop
- Run armature with less weight
- Reduce the temperature of armature
Q23: Why the D.C generator should run in clockwise direction only?
- Protect brushes from damage
- Protect the residual magnetism
- Avoid short circuit in armature
- Avoid over loading of generator
Q24: Why compensating winding is provided in large DC generators?
- Connect more loads
- Reduce commutation effect
- Neutralize armature reaction effect
- Increase the efficiency of generator
Q25: What is the reason for DC generator fails to build up voltage?
- Loose brush contact
- Armature resistance is more
- Field resistance is above critical resistance
- Prime mover is running at above rated speed
Q26: What is the name of generator, if its field is connected in parallel with armature?
- Shunt generator
- Series generator
- Compound generator
- Self excited generator
Q27: What is the purpose of pole shoe in DC generator?
- Reduce the air gap
- Increase the field strength
- Minimize the magnetic losses
- Spread out flux uniformly in the air gap
Q28: What is the function of split rings in DC generator?
- Collects the current unidirectionally
- Maintain constant voltage
- Reduces the voltage drop at brushes
- Increases the terminal voltage than rated
Q29: Which material is used to make brush in generator?
- Carbon and graphite
- Steel and graphite
- Cast iron and graphite
- Aluminium and graphite
Q30: Why DC generators are loosing their residual magnetism?
- Running without load continuously
- Heavy short circuit in load
- Continuous running without break
- Change of direction of rotation very often
Q31: How does the magnetic circuit complete through the yoke and poles in a generator?
- Field coils
- Armature core
- Laminated pole core
- Winding conductors in armature
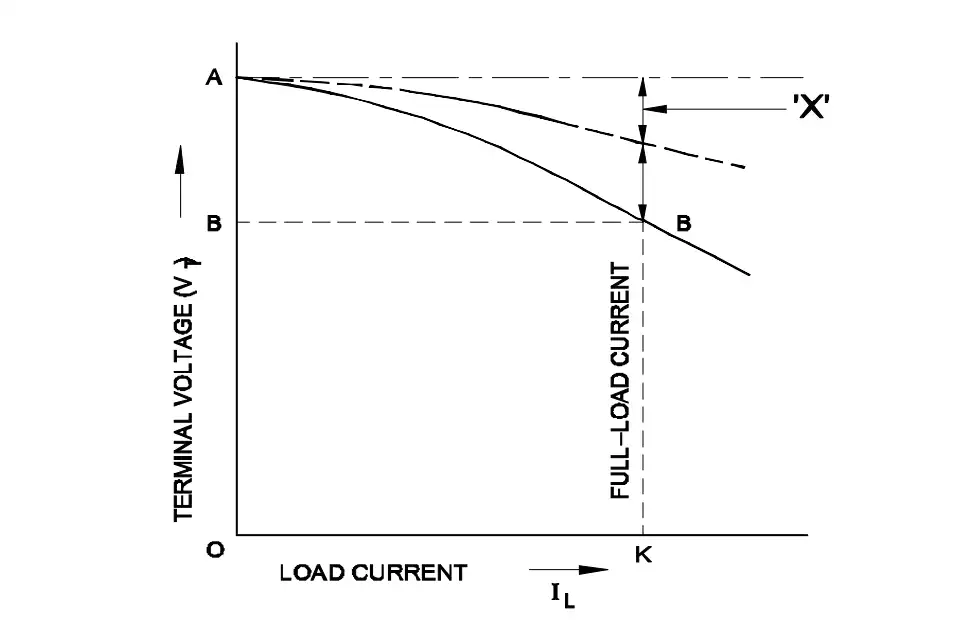
Q32: Why the terminal voltage decreases if load increases in DC shunt generator?
- Because of armature reaction effect
- Due to increased in armature resistance
- Because of brush voltage drop decreases
- Due to increased in shunt field inductance
Q33: Which type of DC generator is used for long distance distribution lines?
- Shunt generator
- Series generator
- Differential compound generator
- Cumulative compound generator
Q34: Which method is used to improve the insulation resistance in DC generator?
- Replacing the brushes frequently
- Heating the machine by running periodically
- Cleaning the commutator segments regularly
- Blowing hot air in to the machine during maintenance
Q35: Which type of D.C Generator works in absence of residual magnetism?
- Shunt generator
- Series generator
- Compound generator
- Separately excited generator
Q36: Which type of D.C generator is used for arc welding?
- Shunt generator
- Series generator
- Differential compound generator
- Cumulative compound generator
Q37: What is the property of wave winding in D.C generator?
- Low current low voltage
- High current low voltage
- Low current high voltage
- High current high voltage
Q38: What is the purpose of resistance wire used in the commutator connection in D.C. generator?
- Maintain constant voltage
- Nullifying statically induced emf
- Increasing statically induced emf
- Smooth reversal of current direction
Q39: Why solid pole core are used in D.C generator?
- To reduce the copper loss
- To increase the residual magnetism
- To decrease the residual magnetism
- To reduce the reluctance of magnetic path
Q40: Which metal is used to make large capacity DC generator yoke?
- Cast iron
- Soft iron
- Aluminium
- Rolled Steel
Q41: What is the function of split rings in a D.C generator?
- Supplies output continuously
- Makes output in the uni direction
- Makes output in the opposite direction
- Collects the output from alternate conductors
Q42: Which type of voltage is induced dynamically in a D.C generator?
- Pulsating voltage
- Oscillating voltage
- Alternating voltage
- Direct current voltage
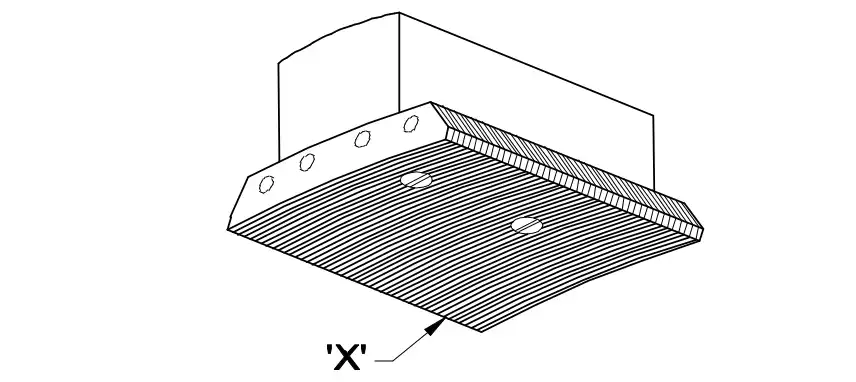
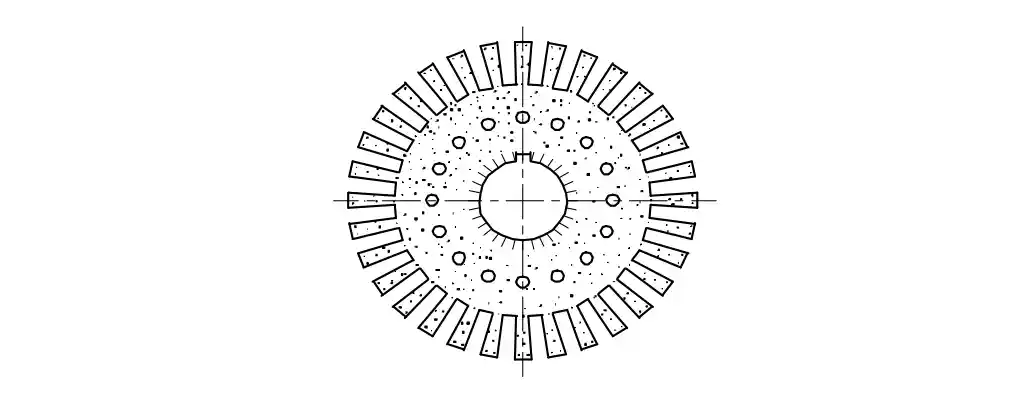
Q43: What is the purpose of slot marked as 'X'?
- To fix the key way
- To make air circulation
- For lubrication purpose
- For easy removal from shaft
Q44: What is the purpose of field coils in D.C generator?
- To increase the flux in air gap
- To decrease the magnetizing current
- To magnetize the poles to produce coil flux
- To increase the reluctance of magnetic path
Q45: Which metal is used to make pole core of large DC generator machines?
- Soft iron
- Cast iron
- Cast steel
- Stainless steel
Q46: Why the pole core stampings are laminated in DC generator?
- Reduce the friction loss
- Reduce the windage loss
- Reduce the hysteresis loss
- Reduce the eddy current loss
Q47: Which type of DC generator is used for electroplating process?
- Shunt generator
- Series generator
- Differential compound generator
- Cumulative compound generator
Q48: What is the purpose of compensating winding in DC generator?
- Minimizes rough commutation
- Maintain constant output voltage
- Neutralizes the demagnetizing effect
- Decreases the excitation current of field coils
Q49: What is the effect if the shunt field resistance is above critical resistance value in a D.C generator?
- Output voltage is pulsating
- Output voltage is above normal
- Generator fails to build up voltage
- Generator builds up voltage normally
Q50: What is the effect of armature reaction in DC generator?
- Output voltage increases
- Output voltage decreases
- Output voltage is pulsating
- Output voltage will become zero
Q51: Calculate the emf generated in a 4 pole DC generator with simplex wave wound armature has 1020 conductors and driven at a speed of 1500 rpm, the flux/pole is 0.007 webers?
- 178 V
- 243 V
- 357 V
- 428 V
Show Calculation
* Number of poles ($P$) = $4$ * Number of conductors ($Z$) = $1020$ * Speed ($N$) = $1500 \text{ rpm}$ * Flux per pole ($\phi$) = $0.007 \text{ Wb}$ * Winding type = Simplex Wave Wound The generated EMF ($E_g$) in a DC generator is calculated using the formula: $$E_g = \frac{\phi Z N P}{60 A}$$ For a Wave Wound armature, the number of parallel paths ($A$) is always equal to 2, regardless of the number of poles. $$E_g = \frac{0.007 \times 1020 \times 1500 \times 4}{60 \times 2}$$ $$E_g = 357 \text{ Volts}$$Q52: How the effect of armature reaction can be neutralized in large DC generators?
- Using compensating winding
- Providing additional inter poles
- Increasing brush contact resistance
- Adding resistance wires with winding
Q53: What is the effect in D.C generator, if it is kept ideal for long time?
- Field coil resistance increases
- Armature resistance Increases
- Increase the armature reaction
- Looses its residual magnetism
Q54: Calculate the induced emf of 4 pole dynamo having 1000 rpm lap wound and total number of conductors is 600, the flux/ pole is 0.064 wb?
- 160V
- 320V
- 480V
- 640V
Show Calculation
**Formula:** $$E_g = \frac{\phi Z N P}{60 A}$$ $\phi = 0.064 \text{ Wb}$ $Z = 600$ $N = 1000 \text{ rpm}$ $P = 4$ $A = 4$ (For Lap winding, $A = P$) $$E_g = \frac{0.064 \times 600 \times 1000 \times 4}{60 \times 4}$$ $$E_g = 640 \text{ V}$$Q55: What is the effect on induced emf if the main field flux get distorted in DC generator?
- Induced emf increases
- Induced emf decreases
- No change in induced emf
- Induced emf becomes zero
Q56: What is the cause for heavy sparking in brushes of DC generator?
- Short circuit in field winding
- Short circuit in armature winding
- MNA and GNA position changed
- Too much spring tension at brush
Found a mistake or mismatch in the question or answer? Let us know via email.
This post is licensed under CC BY 4.0 by the author.